Higher Synovial Immunohistochemistry Reactivity of IL-17A, Dkk1, and TGF-β1 in Patients with Early Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Could Predict the Use of Biologics
- PMID: 38672170
- PMCID: PMC11048598
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040815
Higher Synovial Immunohistochemistry Reactivity of IL-17A, Dkk1, and TGF-β1 in Patients with Early Psoriatic Arthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis Could Predict the Use of Biologics
Abstract
Background: Delay in diagnosis and therapy in patients with arthritis commonly leads to progressive articular damage. The study aimed to investigate the immunohistochemical reactivity of synovial cytokines associated with inflammation and the bone erosives/neoformatives processes among individuals diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteoarthritis (OA), and radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (r-axSpA), with the intention of identifying potential biomarkers.
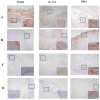
Methods: Specimens were collected from the inflamed knee joints of patients referred for arthroscopic procedures, and the synovial tissue (ST) was prepared for quantifying protein expression through immunohistochemical analysis (% expressed in Ratio_Area-Intensity) for TGF-β1, IL-17A, Dkk1, BMP2, BMP4, and Wnt5b. The collected data underwent thorough analysis and examination of their predictive capabilities utilising receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves.
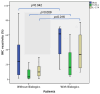
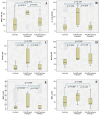
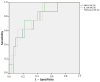
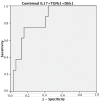
Results: Valid synovial tissue samples were acquired from 40 patients for IHC quantification analysis. Initially, these patients had not undergone treatment with biologics. However, after 5 years, 4 out of 13 patients diagnosed with PsA and two out of nine patients diagnosed with RA had commenced biologic treatments. Individuals with early PsA who received subsequent biologic treatment exhibited significantly elevated IHC reactivity in ST for TGF-β1 (p = 0.015). Additionally, patients with both PsA and RA who underwent biologic therapy displayed increased IHC reactivity for IL-17A (p = 0.016), TGF-β1 (p = 0.009), and Dkk1 (p = 0.042). ROC curve analysis of IHC reactivity for TGF-β1, Dkk1, and IL-17A in the synovial seems to predict future treatment with biologics in the next 5 years with the area under the curve (AUC) of a combined sum of the three values: AUC: 0.828 (95% CI: 0.689-0.968; p 0.005) S 75% E 84.4%.
Conclusions: Higher synovial immunohistochemistry reactivity of IL-17A, Dkk1, and TGF-β1 in patients with early psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis may serve as potential indicators for predicting the necessity of utilising biologic treatments.
Keywords: Dkk1; IHC reactivity; IL-17A; TGF-β1; biomarker; psoriatic arthritis; synovial tissue.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Wnt signaling as a translational target in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 4;23(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06174-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39905450 Free PMC article.
-
Increased synovial immunohistochemistry reactivity of TGF-β1 in erosive peripheral psoriatic arthritis.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023 Mar 30;24(1):246. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06339-4. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023. PMID: 36997896 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneous expression pattern of interleukin 17A (IL-17A), IL-17F and their receptors in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis: possible explanation for nonresponse to anti-IL-17 therapy?Arthritis Res Ther. 2014 Aug 22;16(4):426. doi: 10.1186/s13075-014-0426-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 25146432 Free PMC article.
-
Psoriatic Synovitis: Singularity and Potential Clinical Implications.Front Med (Lausanne). 2019 Feb 11;6:14. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2019.00014. eCollection 2019. Front Med (Lausanne). 2019. PMID: 30805340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic Role of IL-17 and Therapeutic Targeting of IL-17F in Psoriatic Arthritis and Spondyloarthropathies.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 18;24(12):10305. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210305. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373452 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Wnt signaling as a translational target in rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis.J Transl Med. 2025 Feb 4;23(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06174-2. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 39905450 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

