Effect of Granzyme K, FasL and Interferon-γ Expression in Placentas with Preeclampsia
- PMID: 38672196
- PMCID: PMC11048069
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040842
Effect of Granzyme K, FasL and Interferon-γ Expression in Placentas with Preeclampsia
Abstract
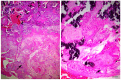
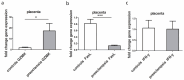
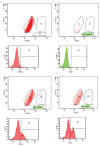
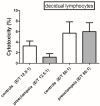
This study aimed to investigate the cytotoxic activity of decidual lymphocytes and the mRNA/protein expression of cytotoxic proteins in various cell types in the context of preeclampsia (PE) compared to those of healthy pregnancies. We analyzed fresh decidua basalis tissue and tissue embedded in paraffin (FFPE) from PE pregnancies (n = 15) and compared them with those of healthy pregnancies (n = 15) of the corresponding gestational age. Using double immunofluorescence staining, we observed differences in the intensity and distribution of staining for granzyme K (GZMK) and FasL in extravillous trophoblasts. RT-qPCR analysis of FFPE placental tissue showed that GZMK mRNA expression was statistically higher (p < 0.0001) in PE compared to that of healthy controls. On the contrary, there was a low expression (p < 0.001) of FasL mRNA in PE compared to controls, while there was no statistically significant difference for IFN-γ mRNA between PE and controls. Although the level of cytotoxic activity changed depending on the ratio of effector and target cells, there was no significant difference observed between PE and controls in this in vitro study. In conclusion, in PE, extravillous trophoblasts exhibited increased expression of GZMK and decreased expression of FasL. These changes may contribute to impaired trophoblast invasion. However, these alterations did not appear to affect the cytotoxic properties of decidual lymphocytes. Additionally, the possibility of cell sorter separation of decidual lymphocytes would greatly contribute to a better understanding of single cells' genetic profiles.
Keywords: FasL; granzyme K; interferon-γ; preeclampsia; trophoblast markers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Decreased Expression of Cytotoxic Proteins in Decidual CD8+ T Cells in Preeclampsia.Biology (Basel). 2021 Oct 13;10(10):1037. doi: 10.3390/biology10101037. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34681139 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal growth restriction is associated with reduced FasL expression by decidual cells.J Reprod Immunol. 2007 Jun;74(1-2):7-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2006.11.002. Epub 2006 Dec 28. J Reprod Immunol. 2007. PMID: 17196256
-
HIF-1α immunohistochemical expression in decidual cells, villous and extravillous trophoblast in placentas from pregnancies complicated with preeclampsia.Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020 Jul;21:176-178. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2020.06.003. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32563172
-
Failure of physiological transformation and spiral artery atherosis: their roles in preeclampsia.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022 Feb;226(2S):S895-S906. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.09.026. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2022. PMID: 32971013 Review.
-
The Role of Interferon (IFN)-γ in Extravillous Trophoblast Cell (EVT) Invasion and Preeclampsia Progression.Reprod Sci. 2023 May;30(5):1462-1469. doi: 10.1007/s43032-022-01110-x. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Reprod Sci. 2023. PMID: 36289172 Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

