Relationships between Osteopontin, Osteoprotegerin, and Other Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Calcifying Arteries
- PMID: 38672202
- PMCID: PMC11048129
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040847
Relationships between Osteopontin, Osteoprotegerin, and Other Extracellular Matrix Proteins in Calcifying Arteries
Abstract
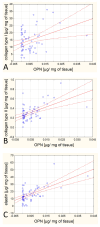
Osteopontin (OPN) and osteoprotegerin (OPG) are glycoproteins that participate in the regulation of tissue biomineralization. The aim of the project is to verify the hypothesis that the content of OPN and OPG in the aorta walls increases with the development of atherosclerosis and that these proteins are quantitatively related to the main proteins in the extracellular arteries matrix. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of the OPN and OPG content in 101 aorta sections have been conducted. Additionally, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) test has been performed to determine the collagen types I-IV and elastin content in the tissues. Correlations between the biochemical data and patients' age/sex, atherosclerosis stages, and calcification occurrences in the tissue have been established. We are the first to report correlations between OPN or OPG and various types of collagen and elastin content (OPG/type I collagen correlation: r = 0.37, p = 0.004; OPG/type II collagen: r = 0.34, p = 0.007; OPG/type III collagen: r = 0.39, p = 0.002, OPG/type IV collagen: r = 0.27, p = 0.03; OPG/elastin: r = 0.42, p = 0.001; OPN/collagen type I: r = 0.34, p = 0.007; OPN/collagen type II: r = 0.52, p = 0.000; OPN/elastin: r = 0.61, p = 0.001). OPN overexpression accompanies calcium deposit (CA) formation with the protein localized in the calcium deposit, whereas OPG is located outside the CA. Although OPN and OPG seem to play a similar function (inhibiting calcification), these glycoproteins have different tissue localizations and independent expression regulation. The independent expression regulation presumably depends on the factors responsible for stimulating the synthesis of collagens and elastin.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; calcification; extracellular matrix proteins; osteopontin; osteoprotegerin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

