The Development of a Regulator of Human Serine Racemase for N-Methyl-D-aspartate Function
- PMID: 38672207
- PMCID: PMC11048566
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040853
The Development of a Regulator of Human Serine Racemase for N-Methyl-D-aspartate Function
Abstract
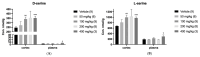
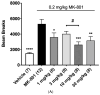
It is crucial to regulate N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) function bivalently depending on the central nervous system (CNS) conditions. CNS disorders with NMDA hyperfunction are involved in the pathogenesis of neurotoxic and/or neurodegenerative disorders with elevated D-serine, one of the NMDA receptor co-agonists. On the contrary, NMDA-enhancing agents have been demonstrated to improve psychotic symptoms and cognition in CNS disorders with NMDA hypofunction. Serine racemase (SR), the enzyme regulating both D- and L-serine levels through both racemization (catalysis from L-serine to D-serine) and β-elimination (degradation of both D- and L-serine), emerges as a promising target for bidirectional regulation of NMDA function. In this study, we explored using dimethyl malonate (DMM), a pro-drug of the SR inhibitor malonate, to modulate NMDA activity in C57BL/6J male mice via intravenous administration. Unexpectedly, 400 mg/kg DMM significantly elevated, rather than decreased (as a racemization inhibitor), D-serine levels in the cerebral cortex and plasma. This outcome prompted us to investigate the regulatory effects of dodecagalloyl-α-D-xylose (α12G), a synthesized tannic acid analog, on SR activity. Our findings showed that α12G enhanced the racemization activity of human SR by about 8-fold. The simulated and fluorescent assay of binding affinity suggested a noncooperative binding close to the catalytic residues, Lys56 and Ser84. Moreover, α12G treatment can improve behaviors associated with major CNS disorders with NMDA hypofunction including hyperactivity, prepulse inhibition deficit, and memory impairment in animal models of positive symptoms and cognitive impairment of psychosis. In sum, our findings suggested α12G is a potential therapeutic for treating CNS disorders with NMDA hypofunction.
Keywords: NMDA; enzyme activator; malonate; racemization; serine racemase; tannic acid; β-elimination.
Conflict of interest statement
This study is supported and funded by SyneuRx International (Taiwan) Corporation. Lu-Ping Lu, Wei-Hua Chang, Yi-Wen Mao, Min-Chi Cheng, Xiao-Yi Zhuang, Chi-Sheng Kuo, Yi-An Lai, and Tsai-Miao Shih are employees of SyneuRx International (Taiwan) Corporation.
Guochuan Emil Tsai is chairman and CEO of SyneuRx International (Taiwan) Corporation.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Conformational flexibility within the small domain of human serine racemase.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2020 Feb 1;76(Pt 2):65-73. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X20001193. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32039887 Free PMC article.
-
ATP binding to human serine racemase is cooperative and modulated by glycine.FEBS J. 2013 Nov;280(22):5853-63. doi: 10.1111/febs.12510. Epub 2013 Sep 25. FEBS J. 2013. PMID: 23992455
-
A new strategy to decrease N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor coactivation: inhibition of D-serine synthesis by converting serine racemase into an eliminase.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Apr 24;98(9):5294-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.091002298. Epub 2001 Apr 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11309496 Free PMC article.
-
Serine Racemase Expression Differentiates Aging from Alzheimer's Brain.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2022;19(7):494-502. doi: 10.2174/1567205019666220805105106. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2022. PMID: 35929621 Review.
-
Inhibition of human serine racemase, an emerging target for medicinal chemistry.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 Jun;12(7):1037-55. doi: 10.2174/138945011795677755. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21291385 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial to the Special Issue "Glycine-(and D-Serine)-Related Neurotransmission: Promising Therapeutic Targets with Still Unsolved Problems".Biomedicines. 2025 May 8;13(5):1140. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13051140. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40426967 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions Involving Glycine and Other Amino Acid Neurotransmitters: Focus on Transporter-Mediated Regulation of Release and Glycine-Glutamate Crosstalk.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 8;12(7):1518. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071518. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062091 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Foltyn V.N., Bendikov I., De Miranda J., Panizzutti R., Dumin E., Shleper M., Li P., Toney M.D., Kartvelishvily E., Wolosker H. Serine racemase modulates intracellular D-serine levels through an alpha, beta-elimination activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2005;280:1754–1763. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405726200. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

