Antitumor Efficacy of Arylquin 1 through Dose-Dependent Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis Induction, and Synergy with Radiotherapy in Glioblastoma Models
- PMID: 38672261
- PMCID: PMC11048020
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040907
Antitumor Efficacy of Arylquin 1 through Dose-Dependent Cytotoxicity, Apoptosis Induction, and Synergy with Radiotherapy in Glioblastoma Models
Abstract
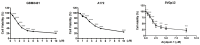
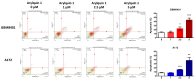
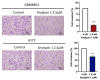
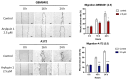
Glioblastoma (GBM), the most aggressive form of brain cancer, is characterized by rapid growth and resistance to conventional therapies. Current treatments offer limited effectiveness, leading to poor survival rates and the need for novel therapeutic strategies. Arylquin 1 has emerged as a potential therapeutic candidate because of its unique mechanism of inducing apoptosis in cancer cells without affecting normal cells. This study investigated the efficacy of Arylquin 1 against GBM using the GBM8401 and A172 cells by assessing its dose-dependent cytotoxicity, apoptosis induction, and synergy with radiotherapy. In vitro assays demonstrated a significant reduction in cell viability and increased apoptosis, particularly at high concentrations of Arylquin 1. Migration and invasion analyses revealed notable inhibition of cellular motility. In vivo experiments on NU/NU nude mice with intracranially implanted GBM cells revealed that Arylquin 1 substantially reduced tumor growth, an effect magnified by concurrent radiotherapy. These findings indicate that by promoting apoptosis and enhancing radiosensitivity, Arylquin 1 is a potent therapeutic option for GBM treatment.
Keywords: Arylquin 1; antitumor efficacy; apoptosis; cytotoxicity; glioblastoma; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

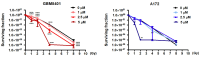
Similar articles
-
Arylquin 1 (Potent Par-4 Secretagogue) Inhibits Tumor Progression and Induces Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 18;23(10):5645. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105645. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628455 Free PMC article.
-
Combined acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid and radiation treatment inhibited glioblastoma tumor cells.PLoS One. 2018 Jul 3;13(7):e0198627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198627. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29969452 Free PMC article.
-
Arylquin 1, a potent Par-4 secretagogue, induces lysosomal membrane permeabilization-mediated non-apoptotic cell death in cancer cells.Toxicol Res. 2019 Nov 21;36(2):167-173. doi: 10.1007/s43188-019-00025-1. eCollection 2020 Apr. Toxicol Res. 2019. PMID: 32257929 Free PMC article.
-
Allyl Isothiocyanate (AITC) Induces Apoptotic Cell Death In Vitro and Exhibits Anti-Tumor Activity in a Human Glioblastoma GBM8401/luc2 Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 8;23(18):10411. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810411. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142326 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol as an antitumor agent for glioblastoma multiforme: Targeting resistance and promoting apoptotic cell deaths.Acta Histochem. 2023 Aug;125(6):152058. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2023.152058. Epub 2023 Jun 17. Acta Histochem. 2023. PMID: 37336070 Review.
References
-
- Ostrom Q.T., Price M., Neff C., Cioffi G., Waite K.A., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2016–2020. Neuro-Oncology. 2023;25((Suppl. S4)):iv1–iv99. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noad149. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wirsching H.G., Galanis E., Weller M. Glioblastoma. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2016;134:381–397. - PubMed
-
- Lacroix M., Abi-Said D., Fourney D.R., Gokaslan Z.L., Shi W., DeMonte F., Lang F.F., McCutcheon I.E., Hassenbusch S.J., Holland E., et al. A multivariate analysis of 416 patients with glioblastoma multiforme: Prognosis, extent of resection, and survival. J. Neurosurg. 2001;95:190–198. doi: 10.3171/jns.2001.95.2.0190. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ostrom Q.T., Gittleman H., Farah P., Ondracek A., Chen Y., Wolinsky Y., Stroup N.E., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS statistical report: Primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro-Oncology. 2013;15((Suppl. S2)):ii1–ii56. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not151. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

