The Phenomenon of Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in the Context of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Treatment: Dynamic and Ever Evolving Subject Matter
- PMID: 38672269
- PMCID: PMC11048092
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines12040915
The Phenomenon of Antiretroviral Drug Resistance in the Context of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Treatment: Dynamic and Ever Evolving Subject Matter
Abstract
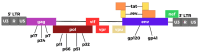
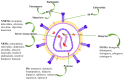
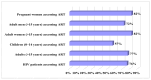
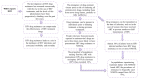
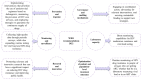
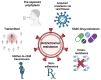
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a significant global health issue that affects a substantial number of individuals across the globe, with a total of 39 million individuals living with HIV/AIDS. ART has resulted in a reduction in HIV-related mortality. Nevertheless, the issue of medication resistance is a significant obstacle in the management of HIV/AIDS. The unique genetic composition of HIV enables it to undergo rapid mutations and adapt, leading to the emergence of drug-resistant forms. The development of drug resistance can be attributed to various circumstances, including noncompliance with treatment regimens, insufficient dosage, interactions between drugs, viral mutations, preexposure prophylactics, and transmission from mother to child. It is therefore essential to comprehend the molecular components of HIV and the mechanisms of antiretroviral medications to devise efficacious treatment options for HIV/AIDS.
Keywords: ART advancements; ART drug resistance; HIV genetic variability; antiretroviral drug resistance; global HIV/AIDS management.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- The Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) Aids in Danger: UNAIDS Global AIDS Update 2022. UNAIDS; Geneva, Switzerland: 2022.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

