Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of the C-Type Lectin Domain Family 4 Member F in Litopenaeus vannamei against White Spot Syndrome Virus
- PMID: 38672285
- PMCID: PMC11047491
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14081137
Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of the C-Type Lectin Domain Family 4 Member F in Litopenaeus vannamei against White Spot Syndrome Virus
Abstract
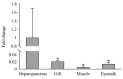
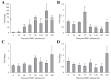
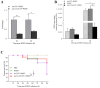
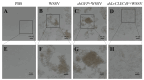
White spot disease (WSD) outbreaks pose a significant threat to the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) farming industry. The causative agent is the white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). There are no effective treatments for WSD so far. Therefore, understanding the resistance mechanisms of L. vannamei against the WSSV is crucial. C-type lectins (CTLs) are important pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that promote agglutination, phagocytosis, encapsulation, bacteriostasis, and antiviral infections. This study cloned the C-type lectin domain family 4 member F (LvCLEC4F) from L. vannamei. LvCLEC4F contains a 492 bp open reading frame (ORF) encoding a protein of 163 amino acids, including a carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD). Following a challenge with the WSSV, the expression profile of LvCLEC4F was significantly altered. Using RNA interference (RNAi) technology, it was found that LvCLEC4F promotes WSSV replication and affects the expression levels of genes related to the regulation of apoptosis, signaling and cellular stress response, and immune defense. Meanwhile, the hemolymph agglutination phenomenon in vivo was weakened when LvCLEC4F was knocked down. These results indicated that LvCLEC4F may play an important role in the interaction between L. vannamei and WSSV.
Keywords: LvCLEC4F; RNAi; WSSV; gene expression; innate immunity; viral disease control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



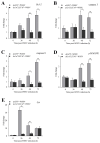
Similar articles
-
Characterization and Expression Analysis of the C-Type Lectin Ladderlectin in Litopenaeus vannamei Post-WSSV Infection.Biology (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;13(10):758. doi: 10.3390/biology13100758. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39452067 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of LvAV in response to white spot syndrome virus infection in the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei).Dev Comp Immunol. 2015 Jul;51(1):48-55. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2015.02.020. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Dev Comp Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25735872
-
Identification of a C-type lectin with antiviral and antibacterial activity from pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei.Dev Comp Immunol. 2014 Oct;46(2):231-40. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2014.04.014. Epub 2014 May 1. Dev Comp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24792214
-
TNF-Receptor-Associated Factor 3 in Litopenaeus vannamei Restricts White Spot Syndrome Virus Infection Through the IRF-Vago Antiviral Pathway.Front Immunol. 2020 Sep 11;11:2110. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02110. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33042123 Free PMC article.
-
Glycogen phosphorylase of shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei): Structure, expression and anti-WSSV function.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Aug;91:275-283. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.05.043. Epub 2019 May 21. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31125663
Cited by
-
Copper Pyrithione Induces Hepatopancreatic Apoptosis and Metabolic Disruption in Litopenaeus vannamei: Integrated Transcriptomic, Metabolomic, and Histopathological Analysis.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;15(14):2134. doi: 10.3390/ani15142134. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723597 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning and characterization of the LvCTL genes encoding C-type lectin from white-leg shrimp ( Litopenaeus vannamei).F1000Res. 2024 Jun 17;12:260. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.126044.3. eCollection 2023. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 39006306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hou C., Song W., Yuan H., Hu N., Tan B., Zhang S. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed that dietary zymosan-A improved the immunity of Penaeus vannamei by regulating the TLR signaling pathway. Aquaculture. 2022;561:738603. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738603. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2022YFF1000304/the National Key R&D Program of China
- 32172960/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CARS-48/the China Agriculture Research System
- 2020TD26/the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS
- 2022SDZG01/the Open Competition Program of Top Ten Critical Priorities of Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation for the 14th Five-Year Plan of Guangdong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

