Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of the C-Type Lectin Domain Family 4 Member F in Litopenaeus vannamei against White Spot Syndrome Virus
- PMID: 38672285
- PMCID: PMC11047491
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14081137
Molecular Characterization and Expression Analysis of the C-Type Lectin Domain Family 4 Member F in Litopenaeus vannamei against White Spot Syndrome Virus
Abstract
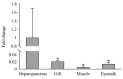
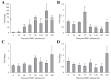
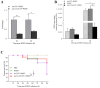
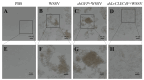
White spot disease (WSD) outbreaks pose a significant threat to the Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) farming industry. The causative agent is the white spot syndrome virus (WSSV). There are no effective treatments for WSD so far. Therefore, understanding the resistance mechanisms of L. vannamei against the WSSV is crucial. C-type lectins (CTLs) are important pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that promote agglutination, phagocytosis, encapsulation, bacteriostasis, and antiviral infections. This study cloned the C-type lectin domain family 4 member F (LvCLEC4F) from L. vannamei. LvCLEC4F contains a 492 bp open reading frame (ORF) encoding a protein of 163 amino acids, including a carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD). Following a challenge with the WSSV, the expression profile of LvCLEC4F was significantly altered. Using RNA interference (RNAi) technology, it was found that LvCLEC4F promotes WSSV replication and affects the expression levels of genes related to the regulation of apoptosis, signaling and cellular stress response, and immune defense. Meanwhile, the hemolymph agglutination phenomenon in vivo was weakened when LvCLEC4F was knocked down. These results indicated that LvCLEC4F may play an important role in the interaction between L. vannamei and WSSV.
Keywords: LvCLEC4F; RNAi; WSSV; gene expression; innate immunity; viral disease control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



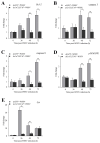
References
-
- Hou C., Song W., Yuan H., Hu N., Tan B., Zhang S. Comparative transcriptome analysis revealed that dietary zymosan-A improved the immunity of Penaeus vannamei by regulating the TLR signaling pathway. Aquaculture. 2022;561:738603. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738603. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 2022YFF1000304/the National Key R&D Program of China
- 32172960/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CARS-48/the China Agriculture Research System
- 2020TD26/the Central Public-interest Scientific Institution Basal Research Fund, CAFS
- 2022SDZG01/the Open Competition Program of Top Ten Critical Priorities of Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation for the 14th Five-Year Plan of Guangdong Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

