Preliminary Results on the Effects of Soybean Isoflavones on Growth Performance and Ruminal Microbiota in Fattening Goats
- PMID: 38672337
- PMCID: PMC11047704
- DOI: 10.3390/ani14081188
Preliminary Results on the Effects of Soybean Isoflavones on Growth Performance and Ruminal Microbiota in Fattening Goats
Abstract
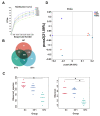
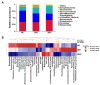
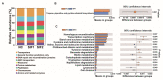
Soybean isoflavones (SIFs), a group of secondary metabolites, have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and hormone-like activities. Supplementation with SIFs in the diet was reported to promote lactation performance in ruminants. The present study was performed to further decipher the effect of various concentrations of SIFs on growth and slaughter performance, serum parameters, meat quality, and ruminal microbiota in fattening goats. After a two-week acclimation, a total of 27 5-month-old Guanzhong male goats (18.29 ± 0.44 kg) were randomly assigned to control (NC), 100 mg/d SIF (SIF1), or 200 mg/d SIF (SIF2) groups. The experimental period lasted 56 days. The weight of the large intestine was greater (p < 0.05) in the SIF1 and SIF2 groups compared with the NC group. Meat quality parameters indicated that SIF1 supplementation led to lower (p < 0.05) cooking loss and shear force (0.05 < p < 0.10). The 16S rRNA sequencing analysis demonstrated that SIF1 supplementation led to lower (p < 0.05) proportions of Papillibacter and Prevotellaceae_UCG-004 but greater (p < 0.05) CAG-352 abundance in the rumen; these responses might have contributed to the improvement in production performance. In conclusion, meat quality and ruminal microbiome could be manipulated in a positive way by oral supplementation with 100 mg/d of SIFs in fattening goats. Thus, this study provides new insights and practical evidence for the introduction of SIFs as a novel additive in goat husbandry.
Keywords: fattening goats; growth performance; ruminal microflora; soybean isoflavones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of Dietary Supplementation With Clostridium butyricum on Growth Performance, Apparent Digestibility, Blood Metabolites, Ruminal Fermentation and Bacterial Communities of Fattening Goats.Front Nutr. 2022 May 24;9:888191. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.888191. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35685891 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of forage type on the rumen microbiota, growth performance, carcass traits, and meat quality in fattening goats.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Apr 27;10:1147685. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1147685. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37180069 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Resveratrol on Growth Performance, Carcass and Meat Quality, Blood Lipid Levels and Ruminal Microbiota in Fattening Goats.Foods. 2022 Feb 18;11(4):598. doi: 10.3390/foods11040598. Foods. 2022. PMID: 35206074 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-omics revealed the long-term effect of ruminal keystone bacteria and the microbial metabolome on lactation performance in adult dairy goats.Microbiome. 2023 Sep 29;11(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s40168-023-01652-5. Microbiome. 2023. PMID: 37773207 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Oils as a Dietary Additive for Small Ruminants: A Meta-Analysis on Performance, Rumen Parameters, Serum Metabolites, and Product Quality.Vet Sci. 2022 Sep 2;9(9):475. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9090475. Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 36136691 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perspective: Isoflavones-Intriguing Molecules but Much Remains to Be Learned about These Soybean Constituents.Adv Nutr. 2025 May;16(5):100418. doi: 10.1016/j.advnut.2025.100418. Epub 2025 Mar 27. Adv Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40157603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Effect of Gastrointestinal Prevotella on Growth Performance Traits in Livestock Animals.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jul 2;14(13):1965. doi: 10.3390/ani14131965. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38998077 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Korma S.A., Li L., Wei W., Liu P., Zhang X., Bakry I.A., An P., Abdrabo K.A.E., Manzoor M.F., Umair M., et al. A Comparative Study of Milk Fat Extracted from the Milk of Different Goat Breeds in China: Fatty Acids, Triacylglycerols and Thermal and Spectroscopic Characterization. Biomolecules. 2022;12:730. doi: 10.3390/biom12050730. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu Z.L., Yang X., Zhang J., Wang W., Liu D., Hou B., Bai T., Zhang R., Zhang Y., Liu H., et al. Effects of forage type on the rumen microbiota, growth performance, carcass traits, and meat quality in fattening goats. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023;10:1147685. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1147685. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

