Uncovering Novel Protein Partners of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Human Testis
- PMID: 38672406
- PMCID: PMC11048102
- DOI: 10.3390/biom14040388
Uncovering Novel Protein Partners of Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase in Human Testis
Abstract
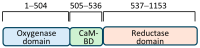
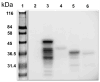
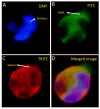
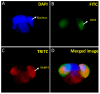
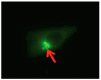
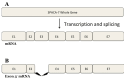
Peroxidative damage to human spermatozoa has been shown to be the primary cause of male infertility. The possible role of nitric oxide (NO) in affecting sperm motility, capacitation, and acrosome reaction has been reported, too. The overproduction of NO by the enzyme inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) could be responsible as it has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases. There have been many studies on regulating iNOS function in various tissues, especially by protein-protein interaction; however, no study has looked for iNOS-interacting proteins in the human testis. Here, we have reported the identification of two proteins that interact with iNOS. We initially undertook a popular yeast two-hybrid assay to screen a human testis cDNA library in yeast using an iNOS-peptide fragment (amino acids 181-335) as bait. We verified our data using the mammalian chemiluminescent co-IP method; first, employing the same peptide and, then, a full-length protein co-expressed in HEK293 cells in addition to the candidate protein. In both cases, these two protein partners of iNOS were revealed: (a) sperm acrosome-associated 7 protein and (b) retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor binding protein.
Keywords: co-immunoprecipitation; male infertility; nitric oxide synthase; protein–protein interaction; yeast two-hybrid assay.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- O’Bryan M.K., Schlatt S., Gerdprasert O., Phillips D.J., de Kretser D.M., Hedger M.P. Inducible nitric oxide synthase in the rat testis: Evidence for potential roles in both normal function and inflammation-mediated infertility. Biol. Reprod. 2000;63:1285–1293. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod63.5.1285. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vidya G., Garg S.P. Role of Nitric Oxide in Male Infertility. J. Indian Acad. Forensic Med. 2011;33:65–68.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

