Drug Cost Avoidance Resulting from Participation in Clinical Trials: A 10-Year Retrospective Analysis of Cancer Patients with Solid Tumors
- PMID: 38672610
- PMCID: PMC11048575
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers16081529
Drug Cost Avoidance Resulting from Participation in Clinical Trials: A 10-Year Retrospective Analysis of Cancer Patients with Solid Tumors
Abstract
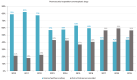
The objective of this single-center retrospective study was to describe the clinical characteristics of adult patients with solid tumors enrolled in cancer clinical trials over a 10-year period (2010-2019) and to assess drug cost avoidance (DCA) associated with sponsors' contributions. The sponsors' contribution to pharmaceutical expenditure was calculated according to the actual price (for each year) of pharmaceutical specialties that the Vall d'Hebron University Hospital (HUVH) would have had to bear in the absence of sponsorship. A total of 2930 clinical trials were conducted with 10,488 participants. There were 140 trials in 2010 and 459 in 2019 (228% increase). Clinical trials of high complexity phase I and basket trials accounted for 34.3% of all trials. There has been a large variation in the pattern of clinical research over the study period, whereas, in 2010, targeted therapy accounted for 79.4% of expenditure and cytotoxic drugs for 20.6%; in 2019, immunotherapy accounted for 68.4%, targeted therapy for 24.4%, and cytotoxic drugs for only 7.1%. A total of four hundred twenty-one different antineoplastic agents were used, the variability of which increased from forty-seven agents in 2010, with only seven of them accounting for 92.8% of the overall pharmaceutical expenditure) to three hundred seventeen different antineoplastic agents in 2019, with thirty-three of them accounting for 90.6% of the overall expenditure. The overall expenditure on antineoplastic drugs in clinical care patients not included in clinical trials was EUR 120,396,096. The total cost of antineoplastic drugs supplied by sponsors in a clinical trial setting was EUR 107,306,084, with a potential DCA of EUR 92,662,609. Overall, clinical trials provide not only the best context for the progress of clinical research and healthcare but also create opportunities for reducing cancer care costs.
Keywords: academic research; clinical trial; drug cost avoidance; pharmaceutical expenditure; solid cancer tumors; sponsor.
Conflict of interest statement
M.-J.C. served as an invited speaker, participated in advisory boards, or received travel grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, Ipsen Pharma, Lilly, and Roche. E.F. served as an invited speaker for Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, Eli Lilly, F.Hoffmann-La Roche, Genentech, Janssen, Medical Trends, Medscape, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp&Dohme, Peervoice, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, and Touch Oncology, as a consultant (advisory board) for Abbvie, Amgen, Astra Zeneca, Bayer, Beigene, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, F.Hoffmann-La Roche, Gilead, Glaxo Smith Kline, Janssen, Merck Serono, Merck Sharp&Dohme, Novartis, Peptomyc, Pfizer, Regeneron, Sanofi, Takeda, Turning Point, and Daiichi Sankyo, received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Astra Zeneca, Janssen, Roche, and served as an independent member of the board for Grifols. M.G. served as an invited speaker or received travel grants from Astra Zeneca, Pfizer, Novartis, and Grifols. E.G. served on research projects for Novartis, Roche, Thermo Fisher, AstraZeneca, Taiho, BeiGene, and Janssen, as a consultant/advisor for Roche, Ellipses Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen Global Services, Seattle Genetics, Thermo Fisher, MabDiscovery, Anaveon, F-Star Therapeutics, Hengrui, Sanofi, Incyte, and Medscape, as a member of the speakers bureau for MSD, Roche, Thermo Fisher, Lilly, Novartis, SeaGen, as an employee of NEXT Oncology, received stock for 1TRIALSP, served as an expert in clinical trials (Institutional) for Adaptimmune LLC., Affimed Gmbh, Amgen SA, Anaveon AG, AstraZeneca AB, Bicycletx Ltd., BioInvent International AB, Biontech SE, Biontech Small Molecules Gmbh, Boehringer Ingelhem International Gmbh, Catalym Gmbh, Cyclacel Biopharmaceuticals, Cytovation AS, Cytomx, F.Hoffmann La Roche Ltd., F-Star Beta Limited, Genentech Inc., Genmab B.V., Hifibio Therapeutics, Hutchison Medipharma Limited, Icon, Imcheck Therapeutics, Immunocore Ltd., Incyte Corporation, Incyte Europe Sàrl, Janssen-Cilag International NV, Janssen-Cilag SA, Laboratorios Servier SL, Medimmune LLC., Merck & Co, Inc., Merck Kgga, Novartis Farmacéutica, S.A, Peptomyc, Pfizer Slu, Relay Therapeutics, Replimmune, Ribon Therapeutics, Ryvu Therapeutics SA, Seattle Genetics Inc., Sotio as, Sqz Biotechnologies, Symphogen A/S, Taiho Pharma Usa Inc., and T-Knife GmbH. J.T. reports personal financial interest in the form of scientific consultancy roles for Alentis Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardiff Oncology, CARSgen Therapeutics, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Genentech Inc., hC Bioscience, Ikena Oncology, Immodulon Therapeutics, Inspirna Inc, Lilly, Menarini, Merck Serono, Merus, MSD, Mirati, Neophore, Novartis, Ona Therapeutics, Orion Biotechnology, Peptomyc, Pfizer, Pierre Fabre, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi, Scandion Oncology, Scorpion Therapeutics, Seattle Genetics, Servier, Sotio Biotech, Taiho, Takeda Oncology, and Tolremo Therapeutics, received stock from Oniria Therapeutics, Alentis Therapeutics, Pangaea Oncology, and 1TRIALSP, and also engaged in educational collaborations with Medscape Education, PeerView Institute for Medical Education, and Physicians Education Resource (PER). C.V. participated in an advisory board for Bayer Hispania SL. The remaining authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Negrouk A., Lacombe D., Cardoso F., Morin F., Carrasco E., Maurel J., Maibach R., Aranda E., Marais R., Stahel R.A. Safeguarding the future of independent, academic clinical cancer research in Europe for the benefit of patients. ESMO Open. 2017;2:e000187. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000187. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency, 1 September 2022, EudraCT Public Web Report for August 2022. [(accessed on 13 November 2023)]. Available online: https://eudract.ema.europa.eu/docs/statistics/EudraCT_Statistics_2022/Eu....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

