Evodiamine Alleviates 2,4-Dinitro-1-Chloro-Benzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms in BALB/c Mice
- PMID: 38672764
- PMCID: PMC11051323
- DOI: 10.3390/life14040494
Evodiamine Alleviates 2,4-Dinitro-1-Chloro-Benzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis-like Symptoms in BALB/c Mice
Abstract
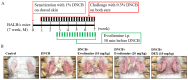
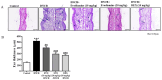
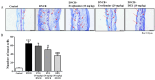
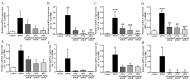
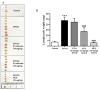
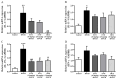
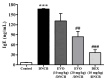
Evodiamine is an alkaloid found in Evodia fruits, a traditional Chinese medicine. Preclinical studies have demonstrated its anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective properties. The 2,4-dinitro-1-chloro-benzene (DNCB) was used to test the effects of evodiamine on a chemically induced atopic dermatitis-like model in BALB/c mice. Evodiamine significantly lowered serum immunoglobulin E levels, which increased as an immune response to the long-term application of DNCB. Several atopic dermatitis-like skin symptoms induced by DNCB, including skin thickening and mast cell accumulation, were suppressed by evodiamine therapy. DNCB induced higher levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in type 2 helper T (Th2) cells (IL-4 and IL-13), Th1 cells (IFN-γ and IL-12A), Th17 cells (IL-17A), Th22 cells (IL-22), and chemokines (IL-6 and IL-8). These increases were suppressed in the lymph nodes and skin following evodiamine treatment. The results of our study indicate that evodiamine suppresses atopic dermatitis-like responses in mice and may therefore be useful in treating these conditions.
Keywords: Evodia rutaecarpa; anti-atopy; atopy; dermatitis; eczema; evodiamine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Silverberg J.I., Barbarot S., Gadkari A., Simpson E.L., Weidinger S., Mina-Osorio P., Rossi A.B., Brignoli L., Saba G., Guillemin I. Atopic dermatitis in the pediatric population: A cross-sectional, international epidemiologic study. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;126:417–428.e412. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.12.020. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wollenberg A., Barbarot S., Bieber T., Christen-Zaech S., Deleuran M., Fink-Wagner A., Gieler U., Girolomoni G., Lau S., Muraro A., et al. Consensus-based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) in adults and children: Part I. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018;32:657–682. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14891. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

