Insights into the Novel Cardiac Biomarker in Acute Heart Failure: Mybp-C
- PMID: 38672783
- PMCID: PMC11051483
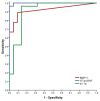
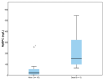
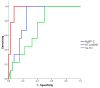
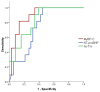
- DOI: 10.3390/life14040513
Insights into the Novel Cardiac Biomarker in Acute Heart Failure: Mybp-C
Abstract
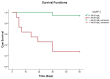
(1) Background: Given its high cardiac specificity and its capacity to directly assess the cardiac function, cardiac myosin-binding protein (MyBP-C) is a promising biomarker in patients with acute heart failure (AHF). The aim of our study was to investigate the clinical utility of this novel marker for diagnosis and short-term prognosis in subjects with AHF. (2) Methods: We measured plasma levels of MyBP-C at admission in 49 subjects (27 patients admitted with AHF and 22 controls). (3) Results: The plasma concentration of MyBP-C was significantly higher in patients with AHF compared to controls (54.88 vs. 0.01 ng/L, p < 0.001). For 30-day prognosis, MyBP-C showed significantly greater AUC (0.972, p < 0.001) than NT-proBNP (0.849, p = 0.001) and hs-TnI (0.714, p = 0.047). In a multivariate logistic regression analysis, an elevated level of MyBP-C was the best independent predictor of 30-day mortality (OR = 1.08, p = 0.039) or combined death/recurrent 30-days rehospitalization (OR = 1.12, p = 0.014). (4) Conclusions: Our data show that circulating MyBP-C is a sensitive and cardiac-specific biomarker with potential utility for the accurate diagnosis and prognosis of AHF.
Keywords: MyBP-C; acute heart failure; biomarker; cardiac myosin-binding protein; diagnosis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac myosin-binding protein C in the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute heart failure.Eur J Heart Fail. 2021 May;23(5):716-725. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2094. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Eur J Heart Fail. 2021. PMID: 33421273
-
Ischemic biomarker heart-type fatty acid binding protein (hFABP) in acute heart failure - diagnostic and prognostic insights compared to NT-proBNP and troponin I.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015 Jun 14;15:50. doi: 10.1186/s12872-015-0026-0. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015. PMID: 26072112 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and Long-Term Prognostic Value of Sensitive Troponin I in Symptomatic Patients Suspected of Acute Heart Failure.Clin Lab. 2015;61(11):1737-47. doi: 10.7754/clin.lab.2015.150503. Clin Lab. 2015. PMID: 26732000
-
The contributions of cardiac myosin binding protein C and troponin I phosphorylation to β-adrenergic enhancement of in vivo cardiac function.J Physiol. 2016 Feb 1;594(3):669-86. doi: 10.1113/JP270959. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26635197 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac myosin binding protein C.Circ Res. 1999 May 28;84(10):1117-26. doi: 10.1161/01.res.84.10.1117. Circ Res. 1999. PMID: 10347086 Review.
Cited by
-
Can Endothelin-1 Help Address the Diagnostic and Prognostic Challenges in Multimorbid Acute Heart Failure Patients?Life (Basel). 2025 Apr 9;15(4):628. doi: 10.3390/life15040628. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40283182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Task Force Members. McDonagh T.A., Metra M., Adamo M., Gardner R.S., Baumbach A., Böhm M., Burri H., Butler J., Čelutkienė J., et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure: Developed by the Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart Failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the Special Contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022;24:4–131. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2333. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

