Assessment of Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury with Machine Learning Tools in Children Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- PMID: 38673539
- PMCID: PMC11050842
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13082266
Assessment of Risk Factors for Acute Kidney Injury with Machine Learning Tools in Children Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Abstract
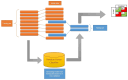
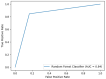
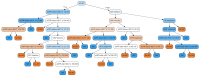
Background: Although acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common complication in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), its prophylaxis remains a clinical challenge. Attempts at prevention or early diagnosis focus on various methods for the identification of factors influencing the incidence of AKI. Our aim was to test the artificial intelligence (AI) potential in the construction of a model defining parameters predicting AKI development. Methods: The analysis covered the clinical data of children followed up for 6 months after HSCT. Kidney function was assessed before conditioning therapy, 24 h after HSCT, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 8 weeks after transplantation, and, finally, 3 and 6 months post-transplant. The type of donor, conditioning protocol, and complications were incorporated into the model. Results: A random forest classifier (RFC) labeled the 93 patients according to presence or absence of AKI. The RFC model revealed that the values of the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) before and just after HSCT, as well as methotrexate use, acute graft versus host disease (GvHD), and viral infection occurrence, were the major determinants of AKI incidence within the 6-month post-transplant observation period. Conclusions: Artificial intelligence seems a promising tool in predicting the potential risk of developing AKI, even before HSCT or just after the procedure.
Keywords: acute graft versus host disease; acute kidney disease; artificial intelligence; random forest classifier; tubular damage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of this study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Raina R., Abu-Arja R., Sethi S.K., Dua R., Chakraborty R., Dibb J.T., Basu R.K., Bissler J., Felix M.B., Brophy P., et al. Acute kidney injury in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Critical appraisal and consensus. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2023;37:1179–1203. doi: 10.1007/s00467-022-05448-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Koh K.N., Sunkara A., Kang G., Sooter A., Mulrooney D.A., Triplett B., Onder A.M., Bissler J., Cunningham L.C. Acute Kidney Injury in Pediatric Patients Receiving Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018;24:758–764. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2017.11.021. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

