A Psychometric Evaluation of the Dysphagia Handicap Index Using Rasch Analysis
- PMID: 38673604
- PMCID: PMC11050868
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13082331
A Psychometric Evaluation of the Dysphagia Handicap Index Using Rasch Analysis
Abstract
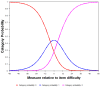
Background/Objectives: The Dysphagia Handicap Index (DHI) is commonly used in oropharyngeal dysphagia (OD) research as a self-report measure of functional health status and health-related quality of life. The DHI was developed and validated using classic test theory. The aim of this study was to use item response theory (Rasch analysis) to evaluate the psychometric properties of the DHI. Methods: Prospective, consecutive patient data were collected at dysphagia or otorhinolaryngology clinics. The sample included 256 adults (53.1% male; mean age 65.2) at risk of OD. The measure's response scale, person and item fit characteristics, differential item functioning, and dimensionality were evaluated. Results: The rating scale was ordered but showed a potential gap in the rating category labels for the overall measure. The overall person (0.91) and item (0.97) reliability was excellent. The overall measure reliably separated persons into at least three distinct groups (person separation index = 3.23) based on swallowing abilities, but the subscales showed inadequate separation. All infit mean squares were in the acceptable range except for the underfitting for item 22 (F). More misfitting was evident in the Z-Standard statistics. Differential item functioning results indicated good performance at an item level for the overall measure; however, contrary to expectation, an OD diagnosis presented only with marginal DIF. The dimensionality of the DHI showed two dimensions in contrast to the three dimensions suggested by the original authors. Conclusions: The DHI failed to reproduce the original three subscales. Caution is needed using the DHI subscales; only the DHI total score should be used. A redevelopment of the DHI is needed; however, given the complexities involved in addressing these issues, the development of a new measure that ensures good content validity may be preferred.
Keywords: Rasch analysis; deglutition; item response theory; measurement; oropharyngeal dysphagia; psychometrics; swallowing disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pacheco-Castilho A.C., Miranda R.P.C., Norberto A.M.Q., Favoretto D.B., Rimoli B.P., Alves L.B.d.M., Weber K.T., Santos T.E.G., Moriguti J.C., Leite J.P., et al. Dysphagia is a strong predictor of death and functional dependence at three months post-stroke. Arq. Neuro-Psiquiatr. 2022;80:462–468. doi: 10.1590/0004-282x-anp-2021-0127. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Speyer R., Balaguer M., Cugy E., Devoucoux C., Morinière S., Soriano G., Vérin E., Woisard V. Expert consensus on clinical decision-making in the disease trajectory of oropharyngeal dysphagia in adults: An international Delphi study. J. Clin. Med. 2023;12:6572. doi: 10.3390/jcm12206572. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous