Ivabradine in Septic Shock: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 38673611
- PMCID: PMC11051007
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13082338
Ivabradine in Septic Shock: A Narrative Review
Abstract
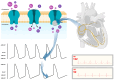
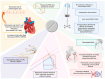
In patients with septic shock, compensatory tachycardia initially serves to maintain adequate cardiac output and tissue oxygenation but may persist despite appropriate fluid and vasopressor resuscitation. This sustained elevation in heart rate and altered heart rate variability, indicative of autonomic dysfunction, is a well-established independent predictor of adverse outcomes in critical illness. Elevated heart rate exacerbates myocardial oxygen demand, reduces ventricular filling time, compromises coronary perfusion during diastole, and impairs the isovolumetric relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle, contributing to ventricular-arterial decoupling. This also leads to increased ventricular and atrial filling pressures, with a heightened risk of arrhythmias. Ivabradine, a highly selective inhibitor of the sinoatrial node's pacemaker current (If or "funny" current), mitigates heart rate by modulating diastolic depolarization slope without affecting contractility. By exerting a selective chronotropic effect devoid of negative inotropic properties, ivabradine shows potential for improving hemodynamics in septic shock patients with cardiac dysfunction. This review evaluates the plausible mechanisms and existing evidence regarding the utility of ivabradine in managing patients with septic shock.
Keywords: MODS; cardiac dysfunction; ivabradine; multiple organ disfunction syndrome; sepsis; septic cardiomyopathy; septic shock; ventriculo-arterial coupling; β-blockers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Evans L., Rhodes A., Alhazzani W., Antonelli M., Coopersmith C.M., French C., Machado F.R., Mcintyre L., Ostermann M., Prescott H.C., et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Intensive Care Med. 2021;47:1181–1247. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Datta P.K., Rewari V., Ramachandran R., Singh P.M., Ray B.R., Aravindan A., Seth S., Parakh N., Trikha A. Effectiveness of Enteral Ivabradine for Heart Rate Control in Septic Shock: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Anaesth. Intensive Care. 2021;49:366–378. doi: 10.1177/0310057X211009913. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

