PlasmaBlade versus Electrocautery for Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Harvesting in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: A Comparative Clinical Outcome Study
- PMID: 38673669
- PMCID: PMC11051315
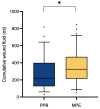
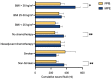
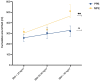
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13082388
PlasmaBlade versus Electrocautery for Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Harvesting in Autologous Breast Reconstruction: A Comparative Clinical Outcome Study
Abstract
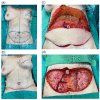
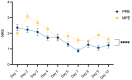
(1) Background: DIEP-based breast reconstruction necessitates wide undermining at the abdominal donor site, creating large wound areas. Flap harvesting is usually conducted using electrosurgical dissection devices. This study sought to compare the clinical outcomes in patients after using the PEAK PlasmaBlade (PPB) versus monopolar electrocautery (MPE). (2) Methods: This retrospective cohort study included 128 patients with DIEP-based breast reconstruction. Patient characteristics and information on the postoperative course were collected and a comparative evaluation was conducted. (3) Results: The MPE group exhibited significantly (p* = 0.0324) higher abdominal drainage volume (351.11 ± 185.96 mL) compared to the PPB group (279.38 ± 183.38 mL). A subgroup analysis demonstrated that PPB significantly reduced postoperative wound fluid in patients with BMI > 30 kg/m2 (p* = 0.0284), without prior neoadjuvant chemotherapy (p** = 0.0041), and among non-smokers (p = 0.0046). Furthermore, postoperative pain was significantly (p**** < 0.0001) lower in the PPB cohort. (4) Conclusions: This study confirms the non-inferiority of the PEAK PlasmaBlade to conventional electrocautery for abdominal flap harvesting. The PPB demonstrated advantages, notably reduced drainage volume and lower postoperative pain levels. Recognizing patient subsets that benefit more from the PPB highlights the importance of personalized device selection based on patient characteristics.
Keywords: PEAK PlasmaBlade; autologous breast reconstruction; clinical outcome; electrosurgery; flap harvesting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of mastectomy and breast reconstruction outcomes using low thermal dissection versus traditional electrocautery: a blinded randomized trial.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jul;188(1):101-106. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06177-9. Epub 2021 Mar 19. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 33742323 Clinical Trial.
-
The use of plasmakinetic cautery compared to conventional electrocautery for dissection of abdominal free flap for breast reconstruction: single-centre, randomized controlled study.Gland Surg. 2019 Jun;8(3):242-248. doi: 10.21037/gs.2018.12.04. Gland Surg. 2019. PMID: 31328103 Free PMC article.
-
Skeletonized internal thoracic artery harvesting: a low thermal damage electrosurgical device provides improved endothelial layer and tendency to better integrity of the vessel wall compared to conventional electrosurgery.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018 Oct 11;13(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13019-018-0797-3. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018. PMID: 30305183 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Literature Review: Robotic-Assisted Harvest of Deep Inferior Epigastric Flap for Breast Reconstruction.Ann Plast Surg. 2022 Dec 1;89(6):703-708. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000003326. Ann Plast Surg. 2022. PMID: 36416707 Review.
-
Economic Analysis of Noninvasive Tissue Oximetry for Postoperative Monitoring of Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction: A Review.Surg Innov. 2020 Oct;27(5):534-542. doi: 10.1177/1553350620942985. Epub 2020 Jul 23. Surg Innov. 2020. PMID: 32701027 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nelson J.A., Allen R.J., Polanco T., Shamsunder M., Patel A.R., McCarthy C.M., Matros E., Dayan J.H., Disa J.J., Cordeiro P.G., et al. Long-Term Patient-Reported Outcomes following Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: An 8-Year Examination of 3268 Patients. Ann. Surg. 2019;270:473–483. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003467. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

