Three-Dimensional Printed Patient-Specific Vestibular Augmentation: A Case Report
- PMID: 38673680
- PMCID: PMC11051386
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm13082408
Three-Dimensional Printed Patient-Specific Vestibular Augmentation: A Case Report
Abstract
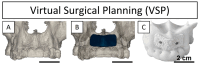
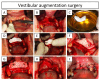
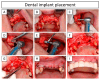
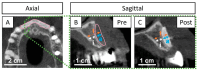
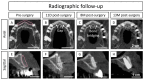
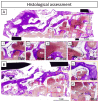
Background: The anterior maxilla is challenging regarding aesthetic rehabilitation. Current bone augmentation techniques are complex and 3D-printed bioceramic bone grafts can simplify the intervention. Aim: A four-teeth defect in the anterior maxilla was reconstructed with a 3D-printed synthetic patient-specific bone graft in a staged approach for dental implant delivery. Methods: The bone graft was designed using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) images. The bone graft was immobilized with fixation screws. Bone augmentation was measured on CBCT images at 11 days and 8 and 13 months post-surgery. A biopsy sample was retrieved at reentry (10 months post-augmentation) and evaluated by histological and micro-computed tomography assessments. The definitive prosthesis was delivered 5 months post-reentry and the patient attended a visit 1-year post-loading. Results: A total bone width of 8 mm was achieved (3.7 mm horizontal bone gain). The reconstructed bone remained stable during the healing period and was sufficient for placing two dental implants (with an insertion torque > 35 N·cm). The fractions of new bone, bone graft, and soft tissue in the biopsy were 40.77%, 41.51%, and 17.72%, respectively. The histological assessment showed no signs of encapsulation, and mature bone was found in close contact with the graft, indicating adequate biocompatibility and suggesting osteoconductive properties of the graft. At 1-year post-loading, the soft tissues were healthy, and the dental implants were stable. Conclusions: The anterior maxilla's horizontal ridge can be reconstructed using a synthetic patient-specific 3D-printed bone graft in a staged approach for implant placement. The dental implants were stable and successful 1-year post-loading.
Keywords: 3D printing; biomaterial; bone grafting; case report; horizontal ridge augmentation; patient-specific; synthetic.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors L.J., M.L., E.T. and Y.R. were employed by the company Mimetis Biomaterials S.L. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Schropp L., Wenzel A., Kostopoulos L., Karring T. Bone Healing and Soft Tissue Contour Changes Following Single-Tooth Extraction: A Clinical and Radiographic 12-Month Prospective Study. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2003;23:313–323. - PubMed
-
- Dong J.K., Jin T.H., Cho H.W., Oh S.C. The Esthetics of the Smile: A Review of Some Recent Studies. Int. J. Prosthodont. 1999;12:9–19. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

