Fine Mapping of Five Grain Size QTLs Which Affect Grain Yield and Quality in Rice
- PMID: 38673733
- PMCID: PMC11050437
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084149
Fine Mapping of Five Grain Size QTLs Which Affect Grain Yield and Quality in Rice
Abstract
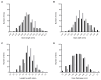
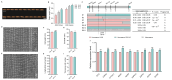
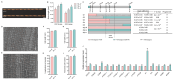
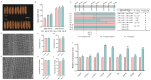
Grain size is a quantitative trait with a complex genetic mechanism, characterized by the combination of grain length (GL), grain width (GW), length to width ration (LWR), and grain thickness (GT). In this study, we conducted quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis to investigate the genetic basis of grain size using BC1F2 and BC1F2:3 populations derived from two indica lines, Guangzhan 63-4S (GZ63-4S) and TGMS29 (core germplasm number W240). A total of twenty-four QTLs for grain size were identified, among which, three QTLs (qGW1, qGW7, and qGW12) controlling GL and two QTLs (qGW5 and qGL9) controlling GW were validated and subsequently fine mapped to regions ranging from 128 kb to 624 kb. Scanning electron microscopic (SEM) analysis and expression analysis revealed that qGW7 influences cell expansion, while qGL9 affects cell division. Conversely, qGW1, qGW5, and qGW12 promoted both cell division and expansion. Furthermore, negative correlations were observed between grain yield and quality for both qGW7 and qGW12. Nevertheless, qGW5 exhibited the potential to enhance quality without compromising yield. Importantly, we identified two promising QTLs, qGW1 and qGL9, which simultaneously improved both grain yield and quality. In summary, our results laid the foundation for cloning these five QTLs and provided valuable resources for breeding rice varieties with high yield and superior quality.
Keywords: QTL; grain size; quality; rice; yield.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Zhao F., Zhang G., Yang Z., He G. Pyramiding QTL for yield-related traits and grain shape in rice using single-segment substitution lines. Indian J. Genet. Pl. Br. 2014;74:496–498. doi: 10.5958/0975-6906.2014.00875.X. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

