Empowering Naringin's Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Nanoencapsulation
- PMID: 38673736
- PMCID: PMC11050564
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084152
Empowering Naringin's Anti-Inflammatory Effects through Nanoencapsulation
Abstract
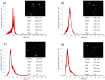
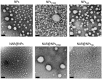
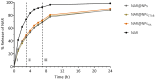
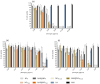
Abundant in citrus fruits, naringin (NAR) is a flavonoid that has a wide spectrum of beneficial health effects, including its anti-inflammatory activity. However, its use in the clinic is limited due to extensive phase I and II first-pass metabolism, which limits its bioavailability. Thus, lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) were used to protect and concentrate NAR in inflamed issues, to enhance its anti-inflammatory effects. To target LNPs to the CD44 receptor, overexpressed in activated macrophages, functionalization with hyaluronic acid (HA) was performed. The formulation with NAR and HA on the surface (NAR@NPsHA) has a size below 200 nm, a polydispersity around 0.245, a loading capacity of nearly 10%, and a zeta potential of about 10 mV. In vitro studies show the controlled release of NAR along the gastrointestinal tract, high cytocompatibility (L929 and THP-1 cell lines), and low hemolytic activity. It was also shown that the developed LNPs can regulate inflammatory mediators. In fact, NAR@NPsHA were able to decrease TNF-α and CCL-3 markers expression by 80 and 90% and manage to inhibit the effects of LPS by around 66% for IL-1β and around 45% for IL-6. Overall, the developed LNPs may represent an efficient drug delivery system with an enhanced anti-inflammatory effect.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory activity; hyaluronic acid; lipid nanoparticles; macrophages; naringin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


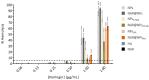
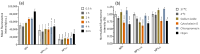


References
-
- Bacanlı M., Başaran A.A., Başaran N. Chapter 4—The Major Flavonoid of Grapefruit: Naringin. In: Watson R.R., Preedy V.R., Zibadi S., editors. Polyphenols: Prevention and Treatment of Human Disease. 2nd ed. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2018. pp. 37–44.
-
- Ribeiro I.A., Rocha J., Sepodes B., Mota-Filipe H., Ribeiro M.H. Effect of naringin enzymatic hydrolysis towards naringenin on the anti-inflammatory activity of both compounds. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2008;52–53:13–18. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2007.10.011. - DOI
-
- Zhang L., Song L., Zhang P., Liu T., Zhou L., Yang G., Lin R., Zhang J. Solubilities of Naringin and Naringenin in Different Solvents and Dissociation Constants of Naringenin. J. Chem. Eng. Data. 2015;60:932–940. doi: 10.1021/je501004g. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

