Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification-Based Lateral Flow Testing for the Detection of Plant Viruses
- PMID: 38673821
- PMCID: PMC11050433
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084237
Isothermal Nucleic Acid Amplification-Based Lateral Flow Testing for the Detection of Plant Viruses
Abstract
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification-based lateral flow testing (INAA-LFT) has emerged as a robust technique for on-site pathogen detection, providing a visible indication of pathogen nucleic acid amplification that rivals or even surpasses the sensitivity of real-time quantitative PCR. The isothermal nature of INAA-LFT ensures consistent conditions for nucleic acid amplification, establishing it as a crucial technology for rapid on-site pathogen detection. However, despite its considerable promise, the widespread application of isothermal INAA amplification-based lateral flow testing faces several challenges. This review provides an overview of the INAA-LFT procedure, highlighting its advancements in detecting plant viruses. Moreover, the review underscores the imperative of addressing the existing limitations and emphasizes ongoing research efforts dedicated to enhancing the applicability and performance of this technology in the realm of rapid on-site testing.
Keywords: LAMP; RPA; detection; isothermal; lateral flow; on-site; plant virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
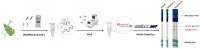

Similar articles
-
CRISPR-Cas assisted diagnostics of plant viruses and challenges.Virology. 2024 Sep;597:110160. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2024.110160. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Virology. 2024. PMID: 38955083 Review.
-
Methods in virus diagnostics: from ELISA to next generation sequencing.Virus Res. 2014 Jun 24;186:20-31. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2013.12.007. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Virus Res. 2014. PMID: 24361981 Review.
-
Current Trends in RNA Virus Detection via Nucleic Acid Isothermal Amplification-Based Platforms.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Feb 11;14(2):97. doi: 10.3390/bios14020097. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection methods for rice viruses by a reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP).Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1236:49-59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-1743-3_5. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25287495
-
Recombinase polymerase amplification applied to plant virus detection and potential implications.Anal Biochem. 2018 Apr 1;546:72-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2018.01.021. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Anal Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29408177 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular insights and diagnostic advances in strawberry-infecting viruses.Front Microbiol. 2025 Aug 6;16:1655696. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1655696. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40842845 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

