Genome-Wide Identification of Glutathione S-Transferase Genes in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Reveals Their Potential Role in Anthocyanin Accumulation on the Fruit Peel
- PMID: 38673847
- PMCID: PMC11050406
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084260
Genome-Wide Identification of Glutathione S-Transferase Genes in Eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) Reveals Their Potential Role in Anthocyanin Accumulation on the Fruit Peel
Abstract
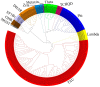
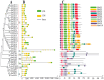
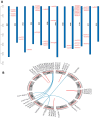
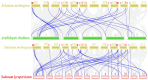
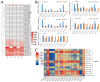
Anthocyanins are ubiquitous pigments derived from the phenylpropanoid compound conferring red, purple and blue pigmentations to various organs of horticultural crops. The metabolism of flavonoids in the cytoplasm leads to the biosynthesis of anthocyanin, which is then conveyed to the vacuoles for storage by plant glutathione S-transferases (GST). Although GST is important for transporting anthocyanin in plants, its identification and characterization in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) remains obscure. In this study, a total of 40 GST genes were obtained in the eggplant genome and classified into seven distinct chief groups based on the evolutionary relationship with Arabidopsis thaliana GST genes. The seven subgroups of eggplant GST genes (SmGST) comprise: dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR), elongation factor 1Bγ (EF1Bγ), Zeta (Z), Theta(T), Phi(F), Tau(U) and tetra-chlorohydroquinone dehalogenase TCHQD. The 40 GST genes were unevenly distributed throughout the 10 eggplant chromosomes and were predominantly located in the cytoplasm. Structural gene analysis showed similarity in exons and introns within a GST subgroup. Six pairs of both tandem and segmental duplications have been identified, making them the primary factors contributing to the evolution of the SmGST. Light-related cis-regulatory elements were dominant, followed by stress-related and hormone-responsive elements. The syntenic analysis of orthologous genes indicated that eggplant, Arabidopsis and tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) counterpart genes seemed to be derived from a common ancestry. RNA-seq data analyses showed high expression of 13 SmGST genes with SmGSTF1 being glaringly upregulated on the peel of purple eggplant but showed no or low expression on eggplant varieties with green or white peel. Subsequently, SmGSTF1 had a strong positive correlation with anthocyanin content and with anthocyanin structural genes like SmUFGT (r = 0.9), SmANS (r = 0.85), SmF3H (r = 0.82) and SmCHI2 (r = 0.7). The suppression of SmGSTF1 through virus-induced gene silencing (VIGs) resulted in a decrease in anthocyanin on the infiltrated fruit surface. In a nutshell, results from this study established that SmGSTF1 has the potential of anthocyanin accumulation in eggplant peel and offers viable candidate genes for the improvement of purple eggplant. The comprehensive studies of the SmGST family genes provide the foundation for deciphering molecular investigations into the functional analysis of SmGST genes in eggplant.
Keywords: SmGSTF1; anthocyanin; eggplant; glutathione S-transferase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of CYP450 genes in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) with a focus on anthocyanin accumlation.BMC Genomics. 2024 Nov 8;25(1):1056. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10990-z. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39511492 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome profiling of genes related to light-induced anthocyanin biosynthesis in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) before purple color becomes evident.BMC Genomics. 2018 Mar 20;19(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-4587-z. BMC Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29554865 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanin accumulation and molecular analysis of anthocyanin biosynthesis-associated genes in eggplant (Solanum melongena L.).J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Apr 2;62(13):2906-12. doi: 10.1021/jf404574c. Epub 2014 Mar 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24654563
-
Genetic and Biotechnological Approaches to Improve Fruit Bioactive Content: A Focus on Eggplant and Tomato Anthocyanins.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 20;25(12):6811. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126811. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide in silico identification of glutathione S-transferase (GST) gene family members in fig (Ficus carica L.) and expression characteristics during fruit color development.PeerJ. 2023 Jan 25;11:e14406. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14406. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 36718451 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anthocyanin pathway in eggplant: genetic regulation and future directions for metabolic engineering.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 May 30;52(1):522. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10597-x. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40445361 Review.
-
Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis reveals the molecular mechanism of exogenous melatonin improves salt tolerance in eggplants.Front Plant Sci. 2025 Jan 10;15:1523582. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1523582. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2025. PMID: 39866315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Han M., Opoku K.N., Bissah N.A.B., Su T. Solanum aethiopicum: The nutrient-rich vegetable crop with great economic, genetic biodiversity and pharmaceutical potential. Horticulturae. 2021;7:126. doi: 10.3390/horticulturae7060126. - DOI
-
- FAOSTAT FAO Statistical Database. 2022. [(accessed on 10 October 2023)]. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

