Novel Ultrastructural Insights into the Clear-Cell Carcinoma of the Pancreas: A Case Report
- PMID: 38673897
- PMCID: PMC11049960
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084313
Novel Ultrastructural Insights into the Clear-Cell Carcinoma of the Pancreas: A Case Report
Abstract
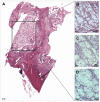
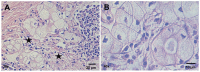
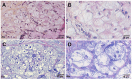
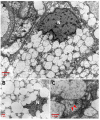
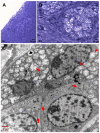
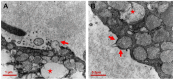
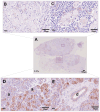
Pancreatic cancer, most frequently as ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC), is the third leading cause of cancer death. Clear-cell primary adenocarcinoma of the pancreas (CCCP) is a rare, aggressive, still poorly characterized subtype of PDAC. We report here a case of a 65-year-old male presenting with pancreatic neoplasia. A histochemical examination of the tumor showed large cells with clear and abundant intracytoplasmic vacuoles. The clear-cell foamy appearance was not related to the hyperproduction of mucins. Ultrastructural characterization with transmission electron microscopy revealed the massive presence of mitochondria in the clear-cell cytoplasm. The mitochondria showed disordered cristae and various degrees of loss of structural integrity. Immunohistochemistry staining for NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] 1 alpha subcomplex, 4-like 2 (NDUFA4L2) proved specifically negative for the clear-cell tumor. Our ultrastructural and molecular data indicate that the clear-cell nature in CCCP is linked to the accumulation of disrupted mitochondria. We propose that this may impact on the origin and progression of this PDAC subtype.
Keywords: clear-cell primary adenocarcinoma; extracellular vesicles; mitochondria; pancreas; transmission electron microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Krebs A.M., Mitschke J., Lasierra Losada M., Schmalhofer O., Boerries M., Busch H., Boettcher M., Mougiakakos D., Reichardt W., Bronsert P., et al. The EMT-activator Zeb1 is a key factor for cell plasticity and promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017;19:518–529. doi: 10.1038/ncb3513. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

