Discovery of Strong 3-Nitro-2-Phenyl- 2H-Chromene Analogues as Antitrypanosomal Agents and Inhibitors of Trypanosoma cruzi Glucokinase
- PMID: 38673904
- PMCID: PMC11050443
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084319
Discovery of Strong 3-Nitro-2-Phenyl- 2H-Chromene Analogues as Antitrypanosomal Agents and Inhibitors of Trypanosoma cruzi Glucokinase
Abstract
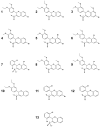
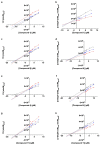
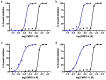
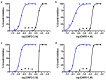
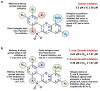
Chagas disease is one of the world's neglected tropical diseases, caused by the human pathogenic protozoan parasite Trypanosoma cruzi. There is currently a lack of effective and tolerable clinically available therapeutics to treat this life-threatening illness and the discovery of modern alternative options is an urgent matter. T. cruzi glucokinase (TcGlcK) is a potential drug target because its product, d-glucose-6-phosphate, serves as a key metabolite in the pentose phosphate pathway, glycolysis, and gluconeogenesis. In 2019, we identified a novel cluster of TcGlcK inhibitors that also exhibited anti-T. cruzi efficacy called the 3-nitro-2-phenyl-2H-chromene analogues. This was achieved by performing a target-based high-throughput screening (HTS) campaign of 13,040 compounds. The selection criteria were based on first determining which compounds strongly inhibited TcGlcK in a primary screen, followed by establishing on-target confirmed hits from a confirmatory assay. Compounds that exhibited notable in vitro trypanocidal activity over the T. cruzi infective form (trypomastigotes and intracellular amastigotes) co-cultured in NIH-3T3 mammalian host cells, as well as having revealed low NIH-3T3 cytotoxicity, were further considered. Compounds GLK2-003 and GLK2-004 were determined to inhibit TcGlcK quite well with IC50 values of 6.1 µM and 4.8 µM, respectively. Illuminated by these findings, we herein screened a small compound library consisting of thirteen commercially available 3-nitro-2-phenyl-2H-chromene analogues, two of which were GLK2-003 and GLK2-004 (compounds 1 and 9, respectively). Twelve of these compounds had a one-point change from the chemical structure of GLK2-003. The analogues were run through a similar primary screening and confirmatory assay protocol to our previous HTS campaign. Subsequently, three in vitro biological assays were performed where compounds were screened against (a) T. cruzi (Tulahuen strain) infective form co-cultured within NIH-3T3 cells, (b) T. brucei brucei (427 strain) bloodstream form, and (c) NIH-3T3 host cells alone. We report on the TcGlcK inhibitor constant determinations, mode of enzyme inhibition, in vitro antitrypanosomal IC50 determinations, and an assessment of structure-activity relationships. Our results reveal that the 3-nitro-2-phenyl-2H-chromene scaffold holds promise and can be further optimized for both Chagas disease and human African trypanosomiasis early-stage drug discovery research.
Keywords: 3-nitro-2-phenyl-2H-chromene analogues; Chagas disease; drug discovery; glucokinase; glucose kinases; hexokinase; human African trypanosomiasis; inhibitors; neglected tropical diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors of this manuscript declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery of antichagasic inhibitors by high-throughput screening with Trypanosoma cruzi glucokinase.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Aug 1;29(15):1948-1953. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.05.037. Epub 2019 May 20. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019. PMID: 31133533
-
Synthesis, biochemical, and biological evaluation of C2 linkage derivatives of amino sugars, inhibitors of glucokinase from Trypanosoma cruzi.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021 Sep 1;47:128227. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2021.128227. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2021. PMID: 34174398
-
Structure-based approach to the identification of a novel group of selective glucosamine analogue inhibitors of Trypanosoma cruzi glucokinase.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2015 Dec;204(2):64-76. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2015.12.004. Epub 2016 Jan 14. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26778112 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis strategies and anti-parasitic evaluation of novel compounds for chagas disease: Advancing drug discovery through structure-activity relationships.Eur J Med Chem. 2025 Feb 15;284:117203. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.117203. Epub 2024 Dec 28. Eur J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39740321 Review.
-
Trypanothione Reductase and Superoxide Dismutase as Current Drug Targets for Trypanosoma cruzi: An Overview of Compounds with Activity against Chagas Disease.Curr Med Chem. 2017 May 31;24(11):1066-1138. doi: 10.2174/0929867323666161227094049. Curr Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28025938 Review.
Cited by
-
TrypPROTACs Unlocking New Therapeutic Strategies for Chagas Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jun 19;18(6):919. doi: 10.3390/ph18060919. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573314 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring bioactive molecules released during inter- and intraspecific competition: A paradigm for novel antiparasitic drug discovery and design for human use.Curr Res Parasitol Vector Borne Dis. 2025 Mar 25;7:100256. doi: 10.1016/j.crpvbd.2025.100256. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Parasitol Vector Borne Dis. 2025. PMID: 40292016 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization, Media Centre Fact Sheets Homepage Updated 2021. [(accessed on 10 March 2024)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chagas-disease-(america...
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Parasites Homepage Updated February 2019. [(accessed on 10 March 2024)]; Available online: http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/chagas/
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

