Assessment of Thyroid Carcinogenic Risk and Safety Profile of GLP1-RA Semaglutide (Ozempic) Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review
- PMID: 38673931
- PMCID: PMC11050669
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084346
Assessment of Thyroid Carcinogenic Risk and Safety Profile of GLP1-RA Semaglutide (Ozempic) Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
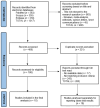
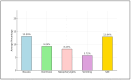
The broadening application of glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 receptor agonists, specifically semaglutide (Ozempic) for the management of diabetes and obesity brings a critical need to evaluate its safety profile, considering estimates of up to 20 million prescriptions per year in the US until 2035. This systematic review aims to assess the incidence of thyroid cancer and detail the spectrum of adverse events associated with semaglutide, focusing on its implications for patient care. Through a systematic search of PubMed, Scopus, and Embase databases up to December 2023, ten randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving 14,550 participants, with 7830 receiving semaglutide, were analyzed, with an additional number of 18 studies that were separately discussed because they reported data from the same RCTs. The review focused on thyroid cancer incidence, gastrointestinal symptoms, and other significant adverse events attributed to semaglutide. The incidence of thyroid cancer in semaglutide-treated patients was less than 1%, suggesting no significant risk. Adverse events were predominantly gastrointestinal, including nausea (2.05% to 19.95%) and diarrhea (1.4% to 13%). Nasopharyngitis and vomiting were also notable, with mean prevalences of 8.23% and 5.97%, respectively. Other adverse events included increased lipase levels (mean of 6.5%), headaches (mean prevalence of 7.92%), decreased appetite (reported consistently at 7%), influenza symptoms (mean prevalence of 5.23%), dyspepsia (mean prevalence of 5.18%), and constipation (mean prevalence of 6.91%). Serious adverse events varied from 7% to 25.2%, highlighting the need for vigilant patient monitoring. These findings underscore the gastrointestinal nature of semaglutide's adverse events, which, while prevalent, did not significantly deter from its clinical benefits in the treatment landscape. This systematic review provides a comprehensive assessment of semaglutide's safety profile, with a focus on gastrointestinal adverse events and a low incidence of thyroid cancer. Despite the prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms, semaglutide remains an efficacious option for managing diabetes and obesity. The detailed characterization of adverse events underscores the importance of monitoring and managing these effects in clinical practice, excluding the hypothesis of carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Ozempic; cancer risk; oncology; semaglutide; thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of semaglutide with reduced incidence and relapse of cannabis use disorder in real-world populations: a retrospective cohort study.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Aug;29(8):2587-2598. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02498-5. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38486046 Free PMC article.
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Harnessing Facebook to Investigate Real-World Mentions of Adverse Events of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist (GLP-1 RA) Medications: Observational Study of Facebook Posts From 2022 to 2024.JMIR Infodemiology. 2025 Jul 24;5:e73619. doi: 10.2196/73619. JMIR Infodemiology. 2025. PMID: 40706081 Free PMC article.
-
Seven glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and polyagonists for weight loss in patients with obesity or overweight: an updated systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Metabolism. 2024 Dec;161:156038. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2024.156038. Epub 2024 Sep 19. Metabolism. 2024. PMID: 39305981
-
Subcutaneously administered tirzepatide vs semaglutide for adults with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials.Diabetologia. 2024 Jul;67(7):1206-1222. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06144-1. Epub 2024 Apr 13. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38613667 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Breast Cancer Using Different Types of Tracers According to Molecular Subtypes and Breast Density-A Randomized Clinical Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Oct 31;14(21):2439. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14212439. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518406 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Use of GLP-1 and GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonists for Respiratory Disorders: Where Are We at?Medicina (Kaunas). 2024 Dec 9;60(12):2030. doi: 10.3390/medicina60122030. Medicina (Kaunas). 2024. PMID: 39768911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaglutide: Double-edged Sword with Risks and Benefits.Arch Intern Med Res. 2025;8(1):1-13. doi: 10.26502/aimr.0189. Epub 2025 Jan 10. Arch Intern Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39902055 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing diagnostic precision in thyroid nodule assessment: evaluating the efficacy of a novel cell preservation technique in fine-needle aspiration cytology.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 27;15:1438063. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1438063. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39280002 Free PMC article.
-
Semaglutide: a key medication for managing cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic syndrome.Future Cardiol. 2025 Jul;21(9):663-683. doi: 10.1080/14796678.2025.2511412. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Future Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40458885 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- O’Neill E.S., Wiegmann A.L., Parrella N., Pittman T., Hood K., Kurlander D. Injectable Weight Loss Medications in Plastic Surgery: What We Know, Perioperative Considerations, and Recommendations for the Future. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2024;12:e5516. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000005516. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Constantino A.K. Ozempic, Wegovy Drug Prescriptions Hit 9 Million, Surge 300% in under Three Years. CNBC. 2023. [(accessed on 14 October 2023)]. Available online: https://www.cnbc.com/2023/09/27/ozempic-wegovy-drug-prescriptions-hit-9-....
-
- Lucas A. Big Food vs. Big pharma: Companies Bet on Snacking Just as Weight Loss Drugs Boom. CNBC. 2023. [(accessed on 14 October 2023)]. Available online: https://www.cnbc.com/2023/10/01/kellanova-bets-on-snacking-as-ozempic-we....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical