The OTX2 Gene Induces Tumor Growth and Triggers Leptomeningeal Metastasis by Regulating the mTORC2 Signaling Pathway in Group 3 Medulloblastomas
- PMID: 38674001
- PMCID: PMC11050316
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084416
The OTX2 Gene Induces Tumor Growth and Triggers Leptomeningeal Metastasis by Regulating the mTORC2 Signaling Pathway in Group 3 Medulloblastomas
Abstract
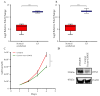
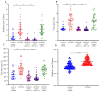
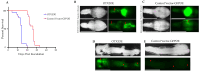
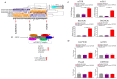
Medulloblastoma (MB) encompasses diverse subgroups, and leptomeningeal disease/metastasis (LMD) plays a substantial role in associated fatalities. Despite extensive exploration of canonical genes in MB, the molecular mechanisms underlying LMD and the involvement of the orthodenticle homeobox 2 (OTX2) gene, a key driver in aggressive MB Group 3, remain insufficiently understood. Recognizing OTX2's pivotal role, we investigated its potential as a catalyst for aggressive cellular behaviors, including migration, invasion, and metastasis. OTX2 overexpression heightened cell growth, motility, and polarization in Group 3 MB cells. Orthotopic implantation of OTX2-overexpressing cells in mice led to reduced median survival, accompanied by the development of spinal cord and brain metastases. Mechanistically, OTX2 acted as a transcriptional activator of the Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) gene's promoter and the mTORC2 signaling pathway, correlating with upregulated downstream genes that orchestrate cell motility and migration. Knockdown of mTOR mRNA mitigated OTX2-mediated enhancements in cell motility and polarization. Analysis of human MB tumor samples (N = 952) revealed a positive correlation between OTX2 and mTOR mRNA expression, emphasizing the clinical significance of OTX2's role in the mTORC2 pathway. Our results reveal that OTX2 governs the mTORC2 signaling pathway, instigating LMD in Group 3 MBs and offering insights into potential therapeutic avenues through mTORC2 inhibition.
Keywords: LMD; OTX2; group 3 medulloblastoma; mTORC2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Characterization of a novel OTX2-driven stem cell program in Group 3 and Group 4 medulloblastoma.Mol Oncol. 2018 Apr;12(4):495-513. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12177. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Mol Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29377567 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cell cycle genes and induction of senescence by overexpression of OTX2 in medulloblastoma cell lines.Mol Cancer Res. 2010 Oct;8(10):1344-57. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0546. Epub 2010 Sep 13. Mol Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21047732
-
A group 3 medulloblastoma stem cell program is maintained by OTX2-mediated alternative splicing.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Aug;26(8):1233-1246. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01460-5. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39025928 Free PMC article.
-
14q22.3 duplication including OTX2 in a girl with medulloblastoma: A case report with literature review.Am J Med Genet A. 2024 Jul;194(7):e63604. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.63604. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Am J Med Genet A. 2024. PMID: 38511879 Review.
-
Discrete signaling mechanisms of mTORC1 and mTORC2: Connected yet apart in cellular and molecular aspects.Adv Biol Regul. 2017 May;64:39-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Jan 4. Adv Biol Regul. 2017. PMID: 28189457 Review.
Cited by
-
The research progress on meningeal metastasis in solid tumors.Discov Oncol. 2025 Feb 28;16(1):254. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-01950-4. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40019647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Medulloblastoma: biology and immunotherapy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 3;16:1602930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1602930. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40677711 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Of travelling homeoproteins and medulloblastomas.Oncogene. 2025 Sep;44(34):3043-3051. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03523-9. Epub 2025 Aug 4. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40760093 Review.
References
-
- Ellison D.W., Dalton J., Kocak M., Nicholson S.L., Fraga C., Neale G., Kenney A.M., Brat D.J., Perry A., Yong W.H., et al. Medulloblastoma: Clinicopathological correlates of SHH, WNT, and non-SHH/WNT molecular subgroups. Acta Neuropathol. 2011;121:381–396. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0800-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kool M., Jones D.T., Jäger N., Northcott P.A., Pugh T.J., Hovestadt V., Piro R.M., Esparza L.A., Markant S.L., Remke M., et al. Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotype-related response to smoothened inhibition. Cancer Cell. 2014;25:393–405. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.02.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kool M., Korshunov A., Remke M., Jones D.T., Schlanstein M., Northcott P.A., Cho Y.J., Koster J., Schouten-van Meeteren A., van Vuurden D., et al. Molecular subgroups of medulloblastoma: An international meta-analysis of transcriptome, genetic aberrations, and clinical data of WNT, SHH, Group 3, and Group 4 medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2012;123:473–484. doi: 10.1007/s00401-012-0958-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

