NF-κB in the Radiation Response of A549 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to X-rays and Carbon Ions under Hypoxia
- PMID: 38674080
- PMCID: PMC11050661
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms25084495
NF-κB in the Radiation Response of A549 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to X-rays and Carbon Ions under Hypoxia
Abstract
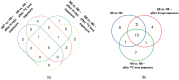
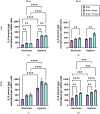
Cellular hypoxia, detectable in up to 80% of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) tumors, is a known cause of radioresistance. High linear energy transfer (LET) particle radiation might be effective in the treatment of hypoxic solid tumors, including NSCLC. Cellular hypoxia can activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB), which can modulate radioresistance by influencing cancer cell survival. The effect of high-LET radiation on NF-κB activation in hypoxic NSCLC cells is unclear. Therefore, we compared the effect of low (X-rays)- and high (12C)-LET radiation on NF-κB responsive genes' upregulation, as well as its target cytokines' synthesis in normoxic and hypoxic A549 NSCLC cells. The cells were incubated under normoxia (20% O2) or hypoxia (1% O2) for 48 h, followed by irradiation with 8 Gy X-rays or 12C ions, maintaining the oxygen conditions until fixation or lysis. Regulation of NF-κB responsive genes was evaluated by mRNA sequencing. Secretion of NF-κB target cytokines, IL-6 and IL-8, was quantified by ELISA. A greater fold change increase in expression of NF-κB target genes in A549 cells following exposure to 12C ions compared to X-rays was observed, regardless of oxygenation status. These genes regulate cell migration, cell cycle, and cell survival. A greater number of NF-κB target genes was activated under hypoxia, regardless of irradiation status. These genes regulate cell migration, survival, proliferation, and inflammation. X-ray exposure under hypoxia additionally upregulated NF-κB target genes modulating immunosurveillance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Increased IL-6 and IL-8 secretion under hypoxia confirmed NF-κB-mediated expression of pro-inflammatory genes. Therefore, radiotherapy, particularly with X-rays, may increase tumor invasiveness in surviving hypoxic A549 cells.
Keywords: 12C ions; A549; IL-6/IL-8 secretion; NF-κB; high-LET radiation; hypoxia-induced radioresistance; p65 (RelA) nuclear localization; tumor hypoxia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
DNA Damage and Inflammatory Response of p53 Null H358 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to X-Ray Exposure Under Chronic Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 23;25(23):12590. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312590. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684302 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia Modulates Radiosensitivity and Response to Different Radiation Qualities in A549 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 13;25(2):1010. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021010. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256084 Free PMC article.
-
Linear Energy Transfer Modulates Radiation-Induced NF-kappa B Activation and Expression of its Downstream Target Genes.Radiat Res. 2018 Apr;189(4):354-370. doi: 10.1667/RR14905.1. Epub 2018 Jan 25. Radiat Res. 2018. PMID: 29369006
-
Hypoxia studies in non‑small cell lung cancer: Pathogenesis and clinical implications (Review).Oncol Rep. 2025 Feb;53(2):29. doi: 10.3892/or.2024.8862. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Oncol Rep. 2025. PMID: 39749693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting inflammatory pathways for tumor radiosensitization.Biochem Pharmacol. 2010 Dec 15;80(12):1904-14. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2010.06.039. Epub 2010 Jun 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20599771 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Particle Therapy to Overcome Cancer Radiation Resistance: "ARCHADE" Consortium Updates in Radiation Biology.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 6;17(9):1580. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091580. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA Damage and Inflammatory Response of p53 Null H358 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells to X-Ray Exposure Under Chronic Hypoxia.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 23;25(23):12590. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312590. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684302 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zegers C.M.L., van Elmpt W., Szardenings K., Kolb H., Waxman A., Subramaniam R.M., Moon D.H., Brunetti J.C., Srinivas S.M., Lambin P., et al. Repeatability of Hypoxia PET Imaging Using [18F]HX4 in Lung and Head and Neck Cancer Patients: A Prospective Multicenter Trial. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2015;42:1840–1849. doi: 10.1007/s00259-015-3100-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- van Elmpt W., Zegers K., Reymen B., Even A.J.G., Dingemans A.-M.C., Öllers M., Wildberger J.E., Mottaghy F.M., Das M., Troost E.G.C., et al. Multiparametric Imaging of Patient and Tumour Heterogeneity in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Quantification of Tumour Hypoxia, Metabolism and Perfusion. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2016;43:240–248. doi: 10.1007/s00259-015-3169-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Postema E.J., McEwan A.J.B., Riauka T.A., Kumar P., Richmond D.A., Abrams D.N., Wiebe L.I. Initial Results of Hypoxia Imaging Using 1-α-D-(5-Deoxy-5-[18F]-Fluoroarabinofuranosyl)-2-Nitroimidazole (18F-FAZA) Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2009;36:1565–1573. doi: 10.1007/s00259-009-1154-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

