Identification and Expression Analysis of the WOX Transcription Factor Family in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.)
- PMID: 38674410
- PMCID: PMC11050393
- DOI: 10.3390/genes15040476
Identification and Expression Analysis of the WOX Transcription Factor Family in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.)
Abstract
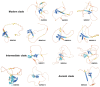
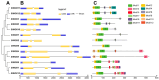
WUSCHEL-related homeobox (WOX) transcription factors are unique to plants and play pivotal roles in plant development and stress responses. In this investigation, we acquired protein sequences of foxtail millet WOX gene family members through homologous sequence alignment and a hidden Markov model (HMM) search. Utilizing conserved domain prediction, we identified 13 foxtail millet WOX genes, which were classified into ancient, intermediate, and modern clades. Multiple sequence alignment results revealed that all WOX proteins possess a homeodomain (HD). The SiWOX genes, clustered together in the phylogenetic tree, exhibited analogous protein spatial structures, gene structures, and conserved motifs. The foxtail millet WOX genes are distributed across 7 chromosomes, featuring 3 pairs of tandem repeats: SiWOX1 and SiWOX13, SiWOX4 and SiWOX5, and SiWOX11 and SiWOX12. Collinearity analysis demonstrated that WOX genes in foxtail millet exhibit the highest collinearity with green foxtail, followed by maize. The SiWOX genes primarily harbor two categories of cis-acting regulatory elements: Stress response and plant hormone response. Notably, prominent hormones triggering responses include methyl jasmonate, abscisic acid, gibberellin, auxin, and salicylic acid. Analysis of SiWOX expression patterns and hormone responses unveiled potential functional diversity among different SiWOX genes in foxtail millet. These findings lay a solid foundation for further elucidating the functions and evolution of SiWOX genes.
Keywords: WOX transcription factor family; expression pattern; foxtail millet; plant hormones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Identification and molecular characterization of MYB Transcription Factor Superfamily in C4 model plant foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.).PLoS One. 2014 Oct 3;9(10):e109920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109920. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25279462 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the DREB gene family in foxtail millet (Setaria Italica L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Apr 5;25(1):432. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06442-9. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40186102 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the bHLH transcription factor family and its response to abiotic stress in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.).BMC Genomics. 2021 Oct 30;22(1):778. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-08095-y. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34717536 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging roles of WOX genes in development and stress responses in woody plants.Plant Sci. 2024 Dec;349:112259. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112259. Epub 2024 Sep 14. Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39284515 Review.
-
Plant Growth Regulators: An Overview of WOX Gene Family.Plants (Basel). 2024 Nov 4;13(21):3108. doi: 10.3390/plants13213108. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39520025 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tissue-Specific Expression Analysis and Functional Validation of SiSCR Genes in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica) Under Hormone and Drought Stresses, and Heterologous Expression in Arabidopsis.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;14(14):2151. doi: 10.3390/plants14142151. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733388 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

