Extended Reality Head-Mounted Displays Are Likely to Pose a Significant Risk in Medical Settings While Current Classification Remains as Non-Critical
- PMID: 38674759
- PMCID: PMC11052361
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12040815
Extended Reality Head-Mounted Displays Are Likely to Pose a Significant Risk in Medical Settings While Current Classification Remains as Non-Critical
Abstract
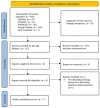
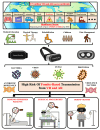
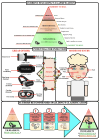
Extended reality (XR) devices, including virtual and augmented reality head-mounted displays (HMDs), are increasingly utilised within healthcare to provide clinical interventions and education. Currently, XR devices are utilised to assist in reducing pain and improving psychological outcomes for immunocompromised patients in intensive care units, palliative care environments and surgical theatres. However, there is a paucity of research on the risks of infection from such devices in healthcare settings. Identify existing literature providing insights into the infection control risk XR HMDs pose within healthcare facilities and the efficacy of current infection control and cleaning procedures. Three databases (PubMed, Embase and CINAHL) in addition to Google Scholar were systematically searched. A total of seven studies were identified for this review. Microorganisms, including pathogenic bacteria (e.g., Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa), were found to be present on XR HMDs. Published cleaning and infection control protocols designed to disinfect XR HMDs and protect users were heterogeneous in nature. Current cleaning protocols displayed varying levels of efficacy with microbial load affected by multiple factors, including time in use, number of users and XR HMD design features. In healthcare settings, fitting XR HMDs harbouring microorganisms near biological and mucosal entry points presents an infection control risk. An urgent revision of the Spaulding classification is required to ensure flexibility that allows for these devices to be reclassified from 'Non-critical' to 'Semi-Critical' depending on the healthcare setting and patient population (surgery, immunocompromised, burns, etc.). This review identified evidence supporting the presence of microorganisms on XR HMDs. Due to the potential for HMDs to contact mucosal entry points, devices must be re-considered within the Spaulding classification as 'Semi-critical'. The existence of microbial contaminated XR HMDs in high-risk medical settings such as operating wards, intensive care units, emergency departments, labour and delivery wards and clinical areas with immunosuppressed patients requires urgent attention. Public health authorities have a duty of care to develop revised guidelines or new recommendations to ensure efficient sanitation of such devices.
Keywords: augmented reality; conjunctivitis; extended reality; fomite; sanitisation; third hand; trojan horse; ultraviolet-C; virtual reality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Augmented, Mixed, and Virtual Reality-Based Head-Mounted Devices for Medical Education: Systematic Review.JMIR Serious Games. 2021 Jul 8;9(3):e29080. doi: 10.2196/29080. JMIR Serious Games. 2021. PMID: 34255668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extended Reality Use in Paediatric Intensive Care: A Scoping Review.J Intensive Care Med. 2023 Sep;38(9):856-877. doi: 10.1177/08850666231185721. Epub 2023 Jul 12. J Intensive Care Med. 2023. PMID: 37437084 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound in augmented reality: a mixed-methods evaluation of head-mounted displays in image-guided interventions.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2020 Nov;15(11):1895-1905. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02236-6. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2020. PMID: 32725398 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Head-Mounted Display Use in Surgery: A Systematic Review.Surg Innov. 2020 Feb;27(1):88-100. doi: 10.1177/1553350619871787. Epub 2019 Sep 12. Surg Innov. 2020. PMID: 31514682
-
Insights and trends review: Use of extended reality (xR) in hand surgery.J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2025 Jun;50(6):762-770. doi: 10.1177/17531934241313208. Epub 2025 Jan 24. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2025. PMID: 39852555 Review.
References
-
- Fortune Business Insights . Virtual Reality (VR in Healthcare Market Size, Share & COVID-19 Impact Analysis, by Component (Hardware, Software, and Content), by Application (Pain Management, Education & Training, Surgery, Paitient Care Management, Rehabilitation & Therapy Procedures, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), and Regional Forecast, 2023–2020. Fortune Business Insights; Pune, India: 2022.
-
- Perkins Coie LLP . Augmented and Virtual Reality Survey Report. Perkins Coie LLP; Washington, DC, USA: 2020.
-
- Barcali E., Iadanza E., Manetti L., Francia P., Nardi C., Bocchi L. Augmented reality in surgery: A scoping review. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:6890. doi: 10.3390/app12146890. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

