Priestia megaterium ASC-1 Isolated from Pickled Cabbage Ameliorates Hyperuricemia by Degrading Uric Acid in Rats
- PMID: 38674776
- PMCID: PMC11052324
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms12040832
Priestia megaterium ASC-1 Isolated from Pickled Cabbage Ameliorates Hyperuricemia by Degrading Uric Acid in Rats
Abstract
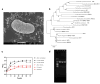
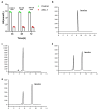
Pickled cabbage, a traditional fermented food rich in functional microorganisms, can effectively control hyperuricemia and gout. In this study, a Priestia megaterium ASC-1 strain with strong uric acid (UA) degradation ability was isolated from pickled cabbage. After oral administration for 15 days, ASC-1 was stably colonized in the rats in this study. ASC-1 significantly reduced UA levels (67.24%) in hyperuricemic rats. Additionally, ASC-1 alleviated hyperuricemia-related inflammatory response, oxidative stress, and blood urea nitrogen. Intestinal microbial diversity results showed that ASC-1 restored intestinal injury and gut flora dysbiosis caused by hyperuricemia. These findings suggest that P. megaterium ASC-1 may be used as a therapeutic adjuvant for the treatment of hyperuricemia.
Keywords: Priestia megaterium; gut microbiota; hyperuricemia; uric acid.
Conflict of interest statement
Siyuan Bi was employed by the Shenzhen Jinyue Test Technology Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Johnson R.J., Bakris G.L., Borghi C., Chonchol M.B., Feldman D., Lanaspa M.A., Merriman T.R., Moe O.W., Mount D.B., Sanchez Lozada L.G., et al. Hyperuricemia, Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Report of a Scientific Workshop Organized by the National Kidney Foundation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018;71:851–865. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.12.009. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

