Surface Modification of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Application in Targeted Delivery Systems of Antitumour Drugs
- PMID: 38675024
- PMCID: PMC11054758
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16081105
Surface Modification of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Application in Targeted Delivery Systems of Antitumour Drugs
Abstract
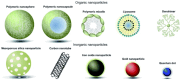
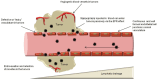
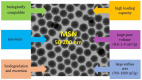
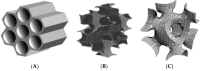
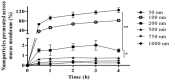
The problem of tumour therapy has attracted the attention of many researchers for many decades. One of the promising strategies for the development of new dosage forms to improve oncology treatment efficacy and minimise side effects is the development of nanoparticle-based targeted transport systems for anticancer drugs. Among inorganic nanoparticles, mesoporous silica deserves special attention due to its outstanding surface properties and drug-loading capability. This review analyses the various factors affecting the cytotoxicity, cellular uptake, and biocompatibility of mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs), constituting a key aspect in the development of safe and effective drug delivery systems. Special attention is paid to technological approaches to chemically modifying MSNs to alter their surface properties. The stimuli that regulate drug release from nanoparticles are also discussed, contributing to the effective control of the delivery process in the body. The findings emphasise the importance of modifying MSNs with different surface functional groups, bio-recognisable molecules, and polymers for their potential use in anticancer drug delivery systems.
Keywords: anticancer drugs; drug delivery; inorganic nanoparticles; mesoporous silica; polymers; surface modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Recent advancements in mesoporous silica nanoparticles towards therapeutic applications for cancer.Acta Biomater. 2019 Apr 15;89:1-13. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.02.031. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30797106 Review.
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: synthesis, classification, drug loading, pharmacokinetics, biocompatibility, and application in drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019 Mar;16(3):219-237. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2019.1575806. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30686075 Review.
-
A Review on Recent Technologies and Patents on Silica Nanoparticles for Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis.Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2020;14(2):126-144. doi: 10.2174/1872211314666200914155051. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 2020. PMID: 32928094 Review.
-
Facile Synthesis of Three Types of Mesoporous Silica Microspheres as Drug Delivery Carriers and their Sustained-Release Properties.Curr Drug Deliv. 2023;20(9):1337-1350. doi: 10.2174/1567201819666220616121602. Curr Drug Deliv. 2023. PMID: 35713141
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles in target drug delivery system: A review.Int J Pharm Investig. 2015 Jul-Sep;5(3):124-33. doi: 10.4103/2230-973X.160844. Int J Pharm Investig. 2015. PMID: 26258053 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Adhesin Antibody-Grafted Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Suppress Immune Escape for Treatment of Fungal Systemic Infection.Molecules. 2024 Sep 25;29(19):4547. doi: 10.3390/molecules29194547. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39407477 Free PMC article.
-
A Review on the Recent Advancements of Polymer-Modified Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery Under Stimuli-Trigger.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;17(12):1640. doi: 10.3390/polym17121640. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40574168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Nanotechnology in TACE Treatment of Liver Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Aug 4;20:9621-9639. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S527518. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40785948 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticle-mediated SIRT1 inhibition suppresses M2 macrophage polarization and hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B.J Nanobiotechnology. 2025 May 27;23(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03447-2. J Nanobiotechnology. 2025. PMID: 40426198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gray E., Figueroa J.D., Oikonomidou O., MacPherson I., Urquhart G., Cameron D.A., Hall P.S. Variation in Chemotherapy Prescribing Rates and Mortality in Early Breast Cancer over Two Decades: A National Data Linkage Study. ESMO Open. 2021;6:100331. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2021.100331. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

