Suitability and Trueness of the Removable Partial Denture Framework Fabricating by Polyether Ether Ketone with CAD-CAM Technology
- PMID: 38675038
- PMCID: PMC11053645
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16081119
Suitability and Trueness of the Removable Partial Denture Framework Fabricating by Polyether Ether Ketone with CAD-CAM Technology
Abstract
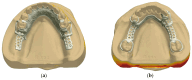
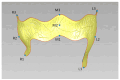
The object of the study was to evaluate the suitability and trueness of the removable partial denture (RPD) framework fabricated by polyether ether ketone (PEEK) with the CAD-CAM technology in vitro. Four different types of dentition defects were selected. In each type, five PEEK RPD frameworks were fabricated by the CAD-CAM technology, while five Co-Cr RPD frameworks were made by traditional casting. The suitability of the framework was evaluated by silicone rubber film slice measurement and the three-dimensional image overlay method. The trueness of the PEEK framework was detected by the three-dimensional image overlay method. Data were statistically analyzed with the use of an independent samples t-test (α = 0.05). The suitability values by silicone rubber film slice measurement of the PEEK group were lower than those of the Co-Cr group in four types, with the differences indicating statistical significance (p < 0.05) in type one, type two, and type four. The suitability values using the three-dimensional image overlay method showed no statistical differences (p > 0.05) between the two groups in four types. The trueness values of the PEEK group were within the allowable range of clinical error. The suitability and trueness of the PEEK RPD framework fabricated by CAD-CAM technology met the requirements of the clinical prosthesis.
Keywords: CAD-CAM; polyether ether ketone; removable partial denture; suitability; trueness.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Virtual Evaluation of the Accuracy of Fit and Trueness in Maxillary Poly(etheretherketone) Removable Partial Denture Frameworks Fabricated by Direct and Indirect CAD/CAM Techniques.J Prosthodont. 2019 Aug;28(7):804-810. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13075. Epub 2019 Jun 11. J Prosthodont. 2019. PMID: 31106495
-
Accuracy of CAD-CAM systems for removable partial denture framework fabrication: A systematic review.J Prosthet Dent. 2021 Feb;125(2):241-248. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2020.01.003. Epub 2020 Mar 5. J Prosthet Dent. 2021. PMID: 32147252
-
Trueness of removable partial denture frameworks additively manufactured with selective laser melting.J Prosthet Dent. 2022 Jan;127(1):122-127. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2020.06.035. Epub 2020 Nov 19. J Prosthet Dent. 2022. PMID: 33223197
-
Effect of Palatal Vault Depth on the Trueness of Metal Laser-Sintered and Cast Cobalt-Chromium Removable Partial Denture Frameworks.J Prosthodont. 2023 Apr;32(4):353-360. doi: 10.1111/jopr.13558. Epub 2022 Jul 6. J Prosthodont. 2023. PMID: 35751546
-
A systematic review of digital removable partial dentures. Part II: CAD/CAM framework, artificial teeth, and denture base.J Prosthodont Res. 2022 Jan 11;66(1):53-67. doi: 10.2186/jpr.JPR_D_20_00117. Epub 2021 Jan 26. J Prosthodont Res. 2022. PMID: 33504722
Cited by
-
Evaluate the clinical performance of Bio-HPP and Vitallium frameworks in free-end removable partial dentures.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 6;15(1):28777. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-11370-7. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40770272 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of Fitting Accuracy of Light- and Auto-Polymerizing Reline Materials Using Three-Dimensional Measurement Techniques.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jan 15;17(2):201. doi: 10.3390/polym17020201. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Revilla-León M., Gómez-Polo M., Vyas S., Barmak A.B., Gallucci G.O., Att W., Özcan M., Krishnamurthy V.R. Artificial Intelligence Models for Tooth-Supported Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics: A Systematic Review. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2023;129:276–292. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2021.06.001. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

