Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Liquid Culture
- PMID: 38675080
- PMCID: PMC11055158
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16081162
Biodegradation of Nitrile Gloves as Sole Carbon Source of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Liquid Culture
Abstract
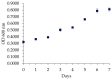
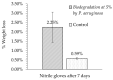
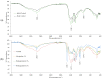
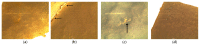
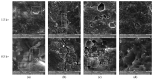
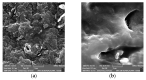
Nitrile gloves have become a significant environmental pollutant after the COVID-19 pandemic due to their single-use design. This study examines the capability of P. aeruginosa to use nitrile gloves as its sole carbon energy source. Biodegradation was determined by P. aeruginosa adapting to increasing nitrile glove concentrations at 1%, 3%, and 5% (w/v). The growth kinetics of P. aeruginosa were evaluated, as well as the polymer weight loss. Topographic changes on the glove surfaces were examined using SEM, and FT-IR was used to evaluate the biodegradation products of the nitrile gloves. Following the establishment of a biofilm on the glove surface, the nitrile toxicity was minimized via biodegradation. The result of the average weight loss of nitrile gloves was 2.25%. FT-IR analysis revealed the presence of aldehydes and aliphatic amines associated with biodegradation. SEM showed P. aeruginosa immersed in the EPS matrix, causing the formation of cracks, scales, protrusions, and the presence of semi-spherical particles. We conclude that P. aeruginosa has the capability to use nitrile gloves as its sole carbon source, even up to 5%, through biofilm formation, demonstrating the potential of P. aeruginosa for the degradation of nitrile gloves.
Keywords: COVID-19; EPS matrix; NBR; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; SEM; biofilm; nitrile gloves; plastic biodegradation; plastic pollution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

