In Situ Reduction of Silver Nanoparticles/Urushiol-Based Polybenzoxazine Composite Coatings with Enhanced Antimicrobial and Antifouling Performances
- PMID: 38675086
- PMCID: PMC11054688
- DOI: 10.3390/polym16081167
In Situ Reduction of Silver Nanoparticles/Urushiol-Based Polybenzoxazine Composite Coatings with Enhanced Antimicrobial and Antifouling Performances
Abstract
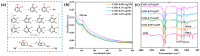
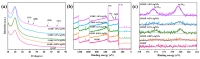
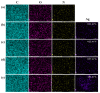
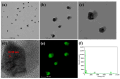
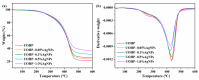
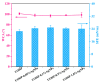
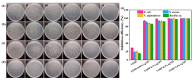
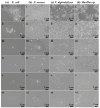
Marine anti-fouling coatings represent an efficient approach to prevent and control the marine biofouling. However, a significant amount of antifouling agent is added to improve the static antifouling performance of the coatings, which leads to an issue whereby static antifouling performance conflicts with eco-friendly traits. Herein, this work reports an in situ reduction synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) within polymers to produce composite coatings, aiming to solve the aforementioned issue. Firstly, urushiol-based benzoxazine monomers were synthesized by the Mannich reaction, using an eco-friendly natural product urushiol and n-octylamine and paraformaldehyde as the reactants. Additionally, AgNPs were obtained through the employment of free radicals formed by phenolic hydroxyl groups in the urushiol-based benzoxazine monomers, achieved by the in situ reduction of silver nitrate in benzoxazine. Then, the urushiol-based benzoxazine/AgNPs composite coatings were prepared by the thermosetting method. AgNPs exhibit broad-spectrum and highly efficient antimicrobial properties, with a low risk to human health and a minimal environmental impact. The composite coating containing a small amount of AgNPs (≤1 wt%) exhibits effective inhibition against various types of bacteria and marine microalgae in static immersion, thereby displaying outstanding antifouling properties. This organic polymer and inorganic nanoparticle composite marine antifouling coating, with its simple preparation method and eco-friendliness, presents an effective solution to the conflict between static antifouling effectiveness and environmental sustainability in marine antifouling coatings.
Keywords: AgNPs; environmentally friendly; in situ reduction; static antifouling; urushiol-based benzoxazine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intrinsic Antibacterial Urushiol-Based Benzoxazine Polymer Coating for Marine Antifouling Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 26;26(9):4118. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094118. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362358 Free PMC article.
-
Facile one-pot synthesis of silver nanoparticles encapsulated in natural polymeric urushiol for marine antifouling.RSC Adv. 2020 Apr 15;10(24):13936-13943. doi: 10.1039/d0ra02205e. eCollection 2020 Apr 6. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35498472 Free PMC article.
-
Urushiol-Based Benzoxazine Containing Sulfobetaine Groups for Sustainable Marine Antifouling Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2023 May 19;15(10):2383. doi: 10.3390/polym15102383. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242960 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on New Environmentally Friendly Antifouling Coatings in Marine Settings: A Review.Biomimetics (Basel). 2023 May 13;8(2):200. doi: 10.3390/biomimetics8020200. Biomimetics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37218786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urushiol-Based Antimicrobial Coatings: Molecular Mechanisms, Structural Innovations, and Multifunctional Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2025 May 28;17(11):1500. doi: 10.3390/polym17111500. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40508743 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intrinsic Antibacterial Urushiol-Based Benzoxazine Polymer Coating for Marine Antifouling Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 26;26(9):4118. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094118. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362358 Free PMC article.
-
Urushiol-Based Coating with High Surface Hydrophilicity for Easy-Cleaning of Oil Pollutants.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Nov 30;16(23):3392. doi: 10.3390/polym16233392. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39684137 Free PMC article.
-
AgNP Composite Silicone-Based Polymer Self-Healing Antifouling Coatings.Materials (Basel). 2024 Aug 30;17(17):4289. doi: 10.3390/ma17174289. Materials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39274679 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Device-Associated Infections Caused by Biofilm-Forming Microbial Pathogens and Controlling Strategies.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Jul 4;13(7):623. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070623. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comprehensive Review on Bio-Based Polybenzoxazines Emphasizing Their Antimicrobial Property.Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 14;13(1):164. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13010164. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 39858931 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qiu H., Feng K., Gapeeva A., Meurisch K., Kaps S., Li X., Yu L., Mishra Y.K., Adelung R., Baum M. Functional polymer materials for modern marine biofouling control. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022;127:101516. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2022.101516. - DOI
-
- Yang W.J., Neoh K.-G., Kang E.-T., Teo S.L.-M., Rittschof D. Polymer brush coatings for combating marine biofouling. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014;39:1017–1042. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2014.02.002. - DOI
-
- Cao P., He X., Xiao J., Yuan C., Bai X. Covalent bonding of AgNPs to 304 stainless steel by reduction in situ for antifouling applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018;452:201–209. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.227. - DOI
-
- Li M.-y., Zhang B.-x., Chen L.-l., Kong J.-j., Wang Y.-f., Ba M. Spontaneous directed leaching of slippery lubricant in self-stratified marine antifouling coatings for nonporous surfaces. Prog. Org. Coat. 2023;184:107858. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2023.107858. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 32301539/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21978050/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020H6029/Fujian Province Science and Technology Project: School-Enterprise Cooperation in Science and Engineering
- FUHJF-L-2022-22/Marine Economic Development Special Fund Project of Fujian Province
- 2022J05234/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

