Mirk/Dyrk1B Kinase Inhibitors in Targeted Cancer Therapy
- PMID: 38675189
- PMCID: PMC11053710
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040528
Mirk/Dyrk1B Kinase Inhibitors in Targeted Cancer Therapy
Abstract
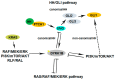
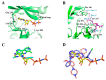
During the last years, there has been an increased effort in the discovery of selective and potent kinase inhibitors for targeted cancer therapy. Kinase inhibitors exhibit less toxicity compared to conventional chemotherapy, and several have entered the market. Mirk/Dyrk1B kinase is a promising pharmacological target in cancer since it is overexpressed in many tumors, and its overexpression is correlated with patients' poor prognosis. Mirk/Dyrk1B acts as a negative cell cycle regulator, maintaining the survival of quiescent cancer cells and conferring their resistance to chemotherapies. Many studies have demonstrated the valuable therapeutic effect of Mirk/Dyrk1B inhibitors in cancer cell lines, mouse xenografts, and patient-derived 3D-organoids, providing a perspective for entering clinical trials. Since the majority of Mirk/Dyrk1B inhibitors target the highly conserved ATP-binding site, they exhibit off-target effects with other kinases, especially with the highly similar Dyrk1A. In this review, apart from summarizing the data establishing Dyrk1B as a therapeutic target in cancer, we highlight the most potent Mirk/Dyrk1B inhibitors recently reported. We also discuss the limitations and perspectives for the structure-based design of Mirk/Dyrk1B potent and highly selective inhibitors based on the accumulated structural data of Dyrk1A and the recent crystal structure of Dyrk1B with AZ191 inhibitor.
Keywords: Mirk/Dyrk1B kinase; X-ray crystal structures; apoptosis; cancer; cancer stem cells; inhibitors; quiescence; targeted cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ovarian cancer cells, not normal cells, are damaged by Mirk/Dyrk1B kinase inhibition.Int J Cancer. 2013 May 15;132(10):2258-69. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27917. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Int J Cancer. 2013. PMID: 23114871 Free PMC article.
-
Mirk/dyrk1B Kinase in Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Mar 8;14(3):5560-75. doi: 10.3390/ijms14035560. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23528858 Free PMC article.
-
Mirk/Dyrk1B mediates G0/G1 to S phase cell cycle progression and cell survival involving MAPK/ERK signaling in human cancer cells.Cancer Cell Int. 2013 Jan 11;13(1):2. doi: 10.1186/1475-2867-13-2. Cancer Cell Int. 2013. PMID: 23311607 Free PMC article.
-
Mirk/Dyrk1B in cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2007 Oct 1;102(2):274-9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21451. J Cell Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17583556 Review.
-
Mirk/Dyrk1B: a multifunctional dual-specificity kinase involved in growth arrest, differentiation, and cell survival.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006;45(3):303-15. doi: 10.1385/CBB:45:3:303. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2006. PMID: 16845176 Review.
Cited by
-
Myocardial DYRK1B Expression Is Increased in Patients with Impaired Cardiac Contractility and Sleep-Disordered Breathing.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jan 29;14(2):163. doi: 10.3390/antiox14020163. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002350 Free PMC article.
-
A safe haven for cancer cells: tumor plus stroma control by DYRK1B.Oncogene. 2025 Feb;44(6):341-347. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03275-6. Epub 2025 Jan 25. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 39863750 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

