Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions for Topical Delivery of Tripeptide-3: From Design of Experiment to Anti-Sebum Efficacy on Facial Skin
- PMID: 38675215
- PMCID: PMC11053593
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16040554
Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions for Topical Delivery of Tripeptide-3: From Design of Experiment to Anti-Sebum Efficacy on Facial Skin
Abstract
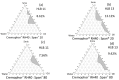
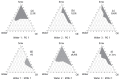
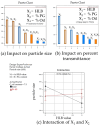
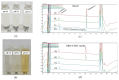
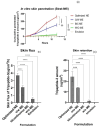
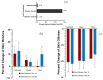
The targeted delivery of a hydrophilic Tripeptide-3 to the skin using microemulsions or nanoemulsions for facial oil reduction was the focus of this study. The impact factors affecting oil/water transparent dispersion formation, such as the surfactant system, HLB value, and co-solvent, were identified through the water titration method and pseudoternary phase diagram plots. The interfacial tension between caprylic/capric triglyceride (CCT oil) and water was significantly reduced by the surfactant/co-surfactant combination (Smix) of Cremophore® RH40 and a double-tails co-surfactant, polyglycerol-3-diisostearate, at an HLB of 13 together with a water-to-co-solvent (PG) ratio of 1:1. A two-level full factorial design of experiment (FFD-DoE) emphasized the independent variables of the HLB value, co-solvent, and CCT oil contents affecting the optimal compositions for micro- or nanoemulsion formation. The low-energy spontaneous emulsification of the optimized combination at a low Smix content (10%) yielded the translucent oil-in-water Tripeptide-3 nanoemulsions with an internal droplet size of 25.7 ± 1.20 nm, a narrow polydispersity index of 0.237 ± 0.129, and 70.6 ± 0.58% transmittance. The in vitro skin permeation study revealed a significantly higher skin penetration and retention of the Tripeptide-3 nanoemulsions compared to the high surfactant microemulsions and coarse emulsions. Skin irritation and oil control efficacy were evaluated in healthy volunteers before and after product application for 28 days. The obtained nanoemulsions not only decreased sebum production but also enhanced skin moisture levels. In conclusion, the meticulously designed nanoemulsions, incorporating suitable excipients, show a promising delivery system for hydrophilic peptides to control sebum overproduction in oily facial skin.
Keywords: Tripeptide-3; anti-sebum; dermal delivery; design of experiment; efficacy; microemulsions; nanoemulsions; oil-control; topical.
Conflict of interest statement
Although the partial fund was provided by SKXL Nature Co., Ltd., the experimental research was conducted independently, and the company had no influence in the experimental setup or the interpretation of the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modification of palm kernel oil esters nanoemulsions with hydrocolloid gum for enhanced topical delivery of ibuprofen.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:4739-47. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S34700. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22973096 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization and characterization of the formation of oil-in-water diazinon nanoemulsions: Modeling and influence of the oil phase, surfactant and sonication.J Environ Sci Health B. 2017 Dec 2;52(12):896-911. doi: 10.1080/03601234.2017.1362941. Epub 2017 Nov 7. J Environ Sci Health B. 2017. PMID: 29111904
-
Formation of stable nanoemulsions by ultrasound-assisted two-step emulsification process for topical drug delivery: Effect of oil phase composition and surfactant concentration and loratadine as ripening inhibitor.Int J Pharm. 2020 Feb 25;576:118952. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118952. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31843549
-
Microemulsions and Nanoemulsions in Skin Drug Delivery.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Apr 5;9(4):158. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9040158. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35447718 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microemulsions as a surrogate carrier for dermal drug delivery.Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009 May;35(5):525-47. doi: 10.1080/03639040802448646. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2009. PMID: 19016057 Review.
Cited by
-
Triple-Loaded Nanoemulsions Incorporating Coffee Extract for the Photoprotection of Curcumin and Capsaicin: Experimental and Computational Evaluation.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 17;17(7):926. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070926. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733134 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Approach in the Development of Chitosan Functionalized Iloperidone Nanoemulsions for Transnasal Delivery, In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Oct 21;25(8):247. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02964-x. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 39433704
-
Nanotechnology-driven nanoemulsion gel for enhanced transdermal delivery of Sophora alopecuroides L. empyreumatic oil: formulation optimization, and anti-biofilm efficacy.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 25;13:1586924. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1586924. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40352356 Free PMC article.
-
Current Approaches in Cosmeceuticals: Peptides, Biotics and Marine Biopolymers.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Mar 18;17(6):798. doi: 10.3390/polym17060798. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40292641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peptides: Emerging Candidates for the Prevention and Treatment of Skin Senescence: A Review.Biomolecules. 2025 Jan 9;15(1):88. doi: 10.3390/biom15010088. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 39858482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bhadra P., Deb A. A Literature review on acne due to hormonal changes and lifestyle. IJONS. 2020;10:18507–18521.
-
- Bukvić Mokos Z., Kralj M., Basta-Juzbašić A., Lakoš Jukić I. Seborrheic dermatitis: An update. ADC. 2012;20:98–104. - PubMed
-
- Wu Y., Niu Y., Zhong S., Liu H., Zhen Y., Saint-Leger D., Verschoore M. A preliminary investigation of the impact of oily skin on quality of life and concordance of self-perceived skin oiliness and skin surface lipids (sebum) Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013;35:442–447. doi: 10.1111/ics.12063. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

