Recent Advances in Carbon Nanotube Utilization in Perovskite Solar Cells: A Review
- PMID: 38675340
- PMCID: PMC11051801
- DOI: 10.3390/mi15040529
Recent Advances in Carbon Nanotube Utilization in Perovskite Solar Cells: A Review
Abstract
Due to their exceptional optoelectronic properties, halide perovskites have emerged as prominent materials for the light-absorbing layer in various optoelectronic devices. However, to increase device performance for wider adoption, it is essential to find innovative solutions. One promising solution is incorporating carbon nanotubes (CNTs), which have shown remarkable versatility and efficacy. In these devices, CNTs serve multiple functions, including providing conducting substrates and electrodes and improving charge extraction and transport. The next iteration of photovoltaic devices, metal halide perovskite solar cells (PSCs), holds immense promise. Despite significant progress, achieving optimal efficiency, stability, and affordability simultaneously remains a challenge, and overcoming these obstacles requires the development of novel materials known as CNTs, which, owing to their remarkable electrical, optical, and mechanical properties, have garnered considerable attention as potential materials for highly efficient PSCs. Incorporating CNTs into perovskite solar cells offers versatility, enabling improvements in device performance and longevity while catering to diverse applications. This article provides an in-depth exploration of recent advancements in carbon nanotube technology and its integration into perovskite solar cells, serving as transparent conductive electrodes, charge transporters, interlayers, hole-transporting materials, and back electrodes. Additionally, we highlighted key challenges and offered insights for future enhancements in perovskite solar cells leveraging CNTs.
Keywords: carbon nanotubes; conducting substrate; green energy; perovskite solar cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

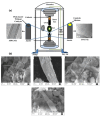
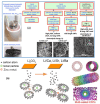
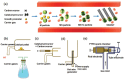
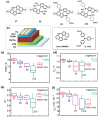


References
-
- Farhan A., Murad M., Qayyum W., Nawaz A., Sajid M., Shahid S., Qamar M.A. Transition-metal sulfides with excellent hydrogen and oxygen reactions: A mini-review. J. Solid State Chem. 2023;329:124445. doi: 10.1016/j.jssc.2023.124445. - DOI
-
- Gielen D., Boshell F., Saygin D., Bazilian M.D., Wagner N., Gorini R. The role of renewable energy in the global energy transformation. Energy Strategy Rev. 2019;24:38–50. doi: 10.1016/j.esr.2019.01.006. - DOI
-
- Huan T.N., Corte D.A.D., Lamaison S., Karapinar D., Lutz L., Menguy N., Foldyna M., Turren-Cruz S.-H., Hagfeldt A., Bella F., et al. Low-cost high-efficiency system for solar-driven conversion of CO2 to hydrocarbons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2019;116:9735–9740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1815412116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sajid M., Qayyum W., Farhan A., Qamar M.A., Nawaz H. Progress in the development of copper oxide-based materials for electrochemical water splitting. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy. 2024;62:209–227. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.02.377. - DOI
-
- Zheng X., Han C., Lee C.-S., Yao W., Zhi C., Tang Y. Materials challenges for aluminum ion based aqueous energy storage devices: Progress and prospects. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024;143:101253. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2024.101253. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

