Updated Progress on Polysaccharides with Anti-Diabetic Effects through the Regulation of Gut Microbiota: Sources, Mechanisms, and Structure-Activity Relationships
- PMID: 38675416
- PMCID: PMC11053653
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17040456
Updated Progress on Polysaccharides with Anti-Diabetic Effects through the Regulation of Gut Microbiota: Sources, Mechanisms, and Structure-Activity Relationships
Abstract
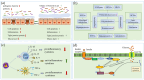
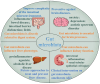
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a common chronic metabolic disease worldwide. The disturbance of the gut microbiota has a complex influence on the development of DM. Polysaccharides are one type of the most important natural components with anti-diabetic effects. Gut microbiota can participate in the fermentation of polysaccharides, and through this, polysaccharides regulate the gut microbiota and improve DM. This review begins by a summary of the sources, anti-diabetic effects and the gut microbiota regulation functions of natural polysaccharides. Then, the mechanisms of polysaccharides in regulating the gut microbiota to exert anti-diabetic effects and the structure-activity relationship are summarized. It is found that polysaccharides from plants, fungi, and marine organisms show great hypoglycemic activities and the gut microbiota regulation functions. The mechanisms mainly include repairing the gut burrier, reshaping gut microbiota composition, changing the metabolites, regulating anti-inflammatory activity and immune function, and regulating the signal pathways. Structural characteristics of polysaccharides, such as monosaccharide composition, molecular weight, and type of glycosidic linkage, show great influence on the anti-diabetic activity of polysaccharides. This review provides a reference for the exploration and development of the anti-diabetic effects of polysaccharides.
Keywords: anti-diabetic effects; mechanism; polysaccharides; structure–activity relationship; the gut microbiota.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Interaction between Mushroom Polysaccharides and Gut Microbiota and Their Effect on Human Health: A Review.Biology (Basel). 2023 Jan 12;12(1):122. doi: 10.3390/biology12010122. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The structure-function relationships and interaction between polysaccharides and intestinal microbiota: A review.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Feb;291:139063. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.139063. Epub 2024 Dec 20. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 39710020 Review.
-
The Effect of Natural Soluble Polysaccharides on the Type 2 Diabetes through Modulating Gut Microbiota: A Review.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(26):5368-5385. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210309110352. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33687877 Review.
-
Potential Application of Marine Fucosyl-Polysaccharides in Regulating Blood Glucose and Hyperglycemic Complications.Foods. 2023 Jul 5;12(13):2600. doi: 10.3390/foods12132600. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37444337 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in dietary polysaccharides as hypoglycemic agents: mechanisms, structural characteristics, and innovative applications.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025;65(8):1383-1403. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2023.2293254. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 38095578 Review.
Cited by
-
In-vitro investigation of antidiabetic and antioxidants properties of major prebiotics and plant based dietary fibers.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 Apr 15;24(1):105. doi: 10.1007/s40200-025-01610-y. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 40248820
-
Evaluating the Efficacy of Secondary Metabolites in Antibiotic-Induced Dysbiosis: A Narrative Review of Preclinical Studies.Antibiotics (Basel). 2025 Feb 1;14(2):138. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics14020138. Antibiotics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40001382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Timbe (Acaciella angustissima) as an Alternative Source of Compounds with Biological Activity: Antidiabetic.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Apr 18;18(4):593. doi: 10.3390/ph18040593. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40284028 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Craciun C.I., Neag M.A., Catinean A., Mitre A.O., Rusu A., Bala C., Roman G., Buzoianu A.D., Muntean D.M., Craciun A.E. The Relationships between Gut Microbiota and Diabetes Mellitus, and Treatments for Diabetes Mellitus. Biomedicines. 2022;10:308. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10020308. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

