Phytochemical Analysis, Biological Activities, and Molecular Docking Studies of Root Extracts from Paeonia Species in Serbia
- PMID: 38675478
- PMCID: PMC11054981
- DOI: 10.3390/ph17040518
Phytochemical Analysis, Biological Activities, and Molecular Docking Studies of Root Extracts from Paeonia Species in Serbia
Abstract
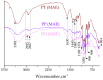
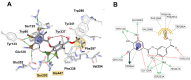
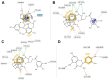
Without being aware of their chemical composition, many cultures have used herbaceous peony roots for medicinal purposes. Modern phytopreparations intended for use in human therapy require specific knowledge about the chemistry of peony roots and their biological activities. In this study, ethanol-water extracts were prepared by maceration and microwave- and ultrasound-assisted extractions (MAE and UAE, respectively) in order to obtain bioactive molecules from the roots of Paeonia tenuifolia L., Paeonia peregrina Mill., and Paeonia officinalis L. wild growing in Serbia. Chemical characterization; polyphenol and flavonoid content; antioxidant, multianti-enzymatic, and antibacterial activities of extracts; and in vitro gastrointestinal digestion (GID) of hot water extracts were performed. The strongest anti-cholinesterase activity was observed in PT extracts. The highest anti-ABTS (2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) radical potential was observed in PP extracts, whereas against DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radicals), the best results were achieved with PO extracts. Regarding antibacterial activity, extracts were strongly potent against Bacillus cereus. A molecular docking simulation was conducted to gather insights into the binding affinity and interactions of polyphenols and other Paeonia-specific molecules in the active sites of tested enzymes. In vitro GID of Paeonia teas showed a different recovery and behavior of the individual bioactives, with an increased recovery of methyl gallate and digallate and a decreased recovery of paeoniflorin and its derivatives. PT (Gulenovci) and PP (Pirot) extracts obtained by UAE and M were more efficient in the majority of the bioactivity assays. This study represents an initial step toward the possible application of Paeonia root extracts in pharmacy, medicine, and food technologies.
Keywords: Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy; antibacterial activity; chemical characterization; enzyme-inhibitory activity; in vitro gastrointestinal digestion; peony roots.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prospective Approaches to the Sustainable Use of Peonies in Bulgaria.Plants (Basel). 2025 Mar 19;14(6):969. doi: 10.3390/plants14060969. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40265918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel source of biologically active compounds - The leaves of Serbian herbaceous peonies.Saudi Pharm J. 2024 Jun;32(6):102090. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2024.102090. Epub 2024 May 3. Saudi Pharm J. 2024. PMID: 38766273 Free PMC article.
-
Chemical Profile and Skin-Beneficial Activities of the Petal Extracts of Paeonia tenuifolia L. from Serbia.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 11;15(12):1537. doi: 10.3390/ph15121537. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36558988 Free PMC article.
-
Paeonia peregrina Mill Petals as a New Source of Biologically Active Compounds: Chemical Characterization and Skin Regeneration Effects of the Extracts.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 21;24(14):11764. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411764. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511520 Free PMC article.
-
Genus Paeonia: A comprehensive review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacological activities, clinical application, and toxicology.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 6;269:113708. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113708. Epub 2020 Dec 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33346027 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic Studies on the Antidiabetic Properties of Gallotannins.Curr Pharm Des. 2025;31(8):575-584. doi: 10.2174/0113816128338114241021110221. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 39501945 Review.
-
Prospective Approaches to the Sustainable Use of Peonies in Bulgaria.Plants (Basel). 2025 Mar 19;14(6):969. doi: 10.3390/plants14060969. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40265918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Synthesis, Characterization, and Biological Evaluation of a Fluorenyl-Methoxycarbonyl-Containing Thioxo-Triazole-Bearing Dipeptide: Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and BSA/DNA Binding Studies for Potential Therapeutic Applications in ROS Scavenging and Drug Transport.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 26;15(7):933. doi: 10.3390/biom15070933. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Oancea S., Perju M., Olosutean H. Influence of Enzyme-Aided Extraction and Ultrasonication on the Phenolics Content and Antioxidant Activity of Paeonia officinalis L. Petals. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2020;85:845–856. doi: 10.2298/JSC190807120O. - DOI
-
- Oancea S., Perju M., Coman D., Olosutean H. Optimization of Conventional and Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction of Paeonia officinalis Anthocyanins, as Natural Alternative for a Green Technology of Cotton Dyeing. Rom. Biotechnol. Lett. 2021;26:2527–2534. doi: 10.25083/rbl/26.2/2527.2534. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

