Spike-Specific Memory B Cell Response in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Recipients following Multiple mRNA-1273 Vaccinations: A Longitudinal Observational Study
- PMID: 38675750
- PMCID: PMC11054563
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines12040368
Spike-Specific Memory B Cell Response in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Recipients following Multiple mRNA-1273 Vaccinations: A Longitudinal Observational Study
Abstract
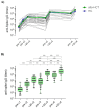
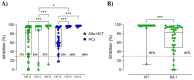
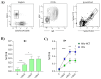
Preventing SARS-CoV-2 infection is of utmost importance in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation patients (allo-HCT), given their heightened susceptibility to adverse outcomes associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, limited data are available regarding the immune response to COVID-19 vaccines in these subjects, particularly concerning the generation and persistence of spike-specific memory response. Here, we analyzed the spike-specific memory B cells in a cohort of allo-HCT recipients vaccinated with multiple doses of the mRNA-1273 vaccine and monitored the spike-specific antibody response from baseline up to one month after the fourth dose. After the primary vaccine series, the frequency of spike-specific B cells, detected within the pool of Ig-switched CD19+ cells, significantly increased. The booster dose further induced a significant expansion, reaching up to 0.28% of spike-specific B cells. The kinetics of this expansion were slower in the allo-HCT recipients compared to healthy controls. Spike-specific IgG and ACE2/RBD binding inhibition activity were observed in 80% of the allo-HCT recipients after the first two doses, with a significant increase after the third and fourth booster doses, including in the subjects who did not respond to the primary vaccine series. Additionally, 87% of the allo-HCT recipients exhibited positive cross-inhibition activity against the BA.1 variant. Our findings provide evidence that allo-HCT recipients need repeated doses of the mRNA-1273 vaccine to induceSARS-CoV-2 specific immune response similar to that observed in healthy individuals. This is particularly crucial for vulnerable individuals who may exhibit a limited response to the primary series of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients; mRNA-based vaccine; spike-specific memory B cells; vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibody Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation.Transplant Cell Ther. 2022 Apr;28(4):214.e1-214.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2022.01.019. Epub 2022 Jan 31. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022. PMID: 35092892 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of neutralizing antibody response to BNT162b2 vaccination in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Oct 24;14(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01190-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34689821 Free PMC article.
-
Specific immune response to mRNA vaccines against COVID-19 in patients receiving allogeneic stem cell transplantation for myeloid malignancy was altered by immunosuppressive therapy.Leuk Res. 2023 Jul;130:107314. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2023.107314. Epub 2023 May 16. Leuk Res. 2023. PMID: 37216792 Free PMC article.
-
Three doses of a recombinant conjugated SARS-CoV-2 vaccine early after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: predicting indicators of a high serologic response-a prospective, single-arm study.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 19;14:1169666. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1169666. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37153556 Free PMC article.
-
Transplant-acquired allergy in HCT-recipients: Reference for clinical management.Blood Rev. 2025 Apr 11:101289. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2025.101289. Online ahead of print. Blood Rev. 2025. PMID: 40234161 Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinal immunogenicity cohort study of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines across individuals with different immunocompromising conditions: heterogeneity in the immune response and crucial role of Omicron-adapted booster doses.EBioMedicine. 2025 Mar;113:105577. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2025.105577. Epub 2025 Feb 4. EBioMedicine. 2025. PMID: 39908650 Free PMC article.
-
Progress and prospects of mRNA-based drugs in pre-clinical and clinical applications.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Nov 14;9(1):322. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-02002-z. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 39543114 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptomic analysis after SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination reveals a specific gene signature in low-responder hemodialysis patients.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 30;16:1508659. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1508659. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40370459 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Varma A., Kosuri S., Ustun C., Ibrahim U., Moreira J., Bishop M.R., Nathan S., Mehta J., Moncayo D., Heng J., et al. COVID-19 Infection in Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Age, Time from Transplant and Steroids Matter. Leukemia. 2020;34:2809–2812. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01019-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sharma A., Bhatt N.S., St Martin A., Abid M.B., Bloomquist J., Chemaly R.F., Dandoy C., Gauthier J., Gowda L., Perales M.-A., et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of COVID-19 in Haematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation Recipients: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet Haematol. 2021;8:e185–e193. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(20)30429-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lafarge A., Mabrouki A., Yvin E., Bredin S., Binois Y., Clere-Jehl R., Azoulay E. Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Immunocompromised Patients: A Comprehensive Review of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Recipients. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care. 2022;28:83–89. doi: 10.1097/MCC.0000000000000907. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cordonnier C., Einarsdottir S., Cesaro S., Di Blasi R., Mikulska M., Rieger C., de Lavallade H., Gallo G., Lehrnbecher T., Engelhard D., et al. Vaccination of Haemopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients: Guidelines of the 2017 European Conference on Infections in Leukaemia (ECIL 7) Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019;19:e200–e212. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30600-5. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

