Community Structure, Drivers, and Potential Functions of Different Lifestyle Viruses in Chaohu Lake
- PMID: 38675931
- PMCID: PMC11053968
- DOI: 10.3390/v16040590
Community Structure, Drivers, and Potential Functions of Different Lifestyle Viruses in Chaohu Lake
Abstract
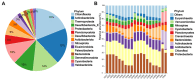
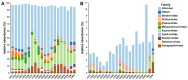
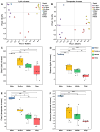
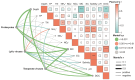
Viruses, as the most prolific entities on Earth, constitute significant ecological groups within freshwater lakes, exerting pivotal ecological roles. In this study, we selected Chaohu Lake, a representative eutrophic freshwater lake in China, as our research site to explore the community distribution, driving mechanisms, and potential ecological functions of diverse viral communities, the intricate virus-host interaction systems, and the overarching influence of viruses on global biogeochemical cycling.
Keywords: Chaohu Lake viruses; auxiliary metabolic genes (AMGs); lytic viruses; temperate viruses; virus community structure; virus–host linkage.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Eutrophication impacts the distribution and functional traits of viral communities in lakes.Sci Total Environ. 2024 Oct 10;946:174339. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2024.174339. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Sci Total Environ. 2024. PMID: 38960155
-
Seasonal succession, host associations, and biochemical roles of aquatic viruses in a eutrophic lake plagued by cyanobacterial blooms.Environ Int. 2024 Nov;193:109125. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2024.109125. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Environ Int. 2024. PMID: 39547087
-
Metatranscriptomic analysis reveals dissimilarity in viral community activity between an ice-free and ice-covered winter in Lake Erie.mSystems. 2024 Jul 23;9(7):e0075324. doi: 10.1128/msystems.00753-24. Epub 2024 Jun 28. mSystems. 2024. PMID: 38940524 Free PMC article.
-
Viruses in Polar Lake and Soil Ecosystems.Adv Virus Res. 2018;101:39-54. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2018.02.002. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Adv Virus Res. 2018. PMID: 29908593 Review.
-
[Effects of global climate change on the ecological characteristics and biogeochemical significance of marine viruses--A review].Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2015 Sep 4;55(9):1097-104. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26762022 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Review of Methods for Studying Viruses in the Environment and Organisms.Viruses. 2025 Jan 11;17(1):86. doi: 10.3390/v17010086. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 39861875 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

