Temporal association between atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 38676601
- PMCID: PMC11590378
- DOI: 10.1177/17474930241253482
Temporal association between atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation (PAF) is strongly associated with ischemic stroke. Continuous cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) can assess PAF episodes over prolonged periods. Studies that attempted to find a temporal association between PAF and ischemic stroke were inconclusive. Thus, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis to assess this relationship.
Aims: This study aimed to assess the temporal association between AF episodes and stroke within 30 days of the arrhythmic episode. The secondary outcome is a temporal association within a 90-day period.
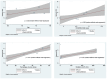
Summary of review: A total of 2804 studies that discussed the temporal relationship between PAF and ischemic stroke were screened, and 7 studies were included in the meta-analysis. Among the 4041 patients included in these studies, there were 138 patients with device detected PAF episodes and stroke. Four studies used a 30-day window for temporality and the pooled odds ratio (OR) showed a significant association (OR 4.11 (95% CI 1.03-16.40)). The three studies reporting on AF and stroke within a 90-day window did not find a significant temporal relationship (OR 0.43 (95% CI 0.13-1.41)). Finally, the pooled result of those seven studies did not show a significant association (OR 1.51 (95% CI 0.44-5.17)).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis supports a temporal relationship between PAF and ischemic stroke within a 30-day window. Establishing this relationship is important for individualized risk prediction and targeted anticoagulation treatment.
Data access statement: The data will be made available upon reasonable request.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; ischemic stroke; paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared the following potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: V.T. receives consulting fees from Medtronic and lecture, and consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and Bayer. H.S.L. reports having received research support from St Jude Medical (now Abbott).
Figures



References
-
- Brambatti M, Connolly SJ, Gold MR, et al.. Temporal relationship between subclinical atrial fibrillation and embolic events. Circulation 2014; 129: 2094–2099. - PubMed
-
- Daoud EG, Glotzer TV, Wyse DG, et al.. Temporal relationship of atrial tachyarrhythmias, cerebrovascular events, and systemic emboli based on stored device data: a subgroup analysis of TRENDS. Heart Rhythm 2011; 8: 1416–1423. - PubMed
-
- Jorfida M, Antolini M, Cerrato E, et al.. Cryptogenic ischemic stroke and prevalence of asymptomatic atrial fibrillation: a prospective study. J Cardiovasc Med 2016; 17: 863–869. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

