Development of a universal cutting guide for raising deep circumflex iliac artery flaps
- PMID: 38676830
- PMCID: PMC11365821
- DOI: 10.1007/s11548-024-03144-9
Development of a universal cutting guide for raising deep circumflex iliac artery flaps
Abstract
Purpose: The deep circumflex iliac crest flap (DCIA) is used for the reconstruction of the jaw. For fitting of the transplant by computer-aided planning (CAD), a computerized tomography (CT) of the jaw and the pelvis is necessary. Ready-made cutting guides save a pelvic CT and healthcare resources while maintaining the advantages of the CAD planning.
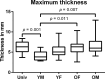
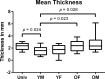
Methods: A total of 2000 CTs of the pelvis were divided into groups of 500 by sex and age (≤ 45 and > 45 years). Three-dimensional (3D) pelvis models were aligned and averaged. Cutting guides were designed on the averaged pelvis for each group and an overall averaged pelvis. The cutting guides and 50 randomly selected iliac crests (10 from each group and 10 from the whole collective) were 3D printed. The appropriate cutting guide was mounted to the iliac crest and a cone beam CT was performed. The thickness of the space between the iliac crest and the cutting guide was evaluated.
Results: Overall the mean thickness of the space was 2.137 mm and the mean volume of the space was 4513 mm3. The measured values were significantly different between the different groups. The overall averaged group had not the greatest volume, maximum thickness and mean thickness of the space.
Conclusion: Ready-made cutting guides for the DCIA flap fit to the iliac crest and make quick and accurate flap raising possible while radiation dose and resources can be saved. The cutting guides fit sufficient to the iliac crest and should keep the advantages of a standard CAD planning.
Keywords: DCIA; DCIA flap; Jaw reconstruction; Oral cancer; VSP, CAM.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Florian Peters, Stefan Raith, Anna Bock, Kristian Kniha, Stephan Christian Möhlhenrich, Marius Heitzer, Frank Hölzle and Ali Modabber have no financial or proprietary interests in any material discussed in this article.
Figures




References
-
- MM Davudov I Harirchi A Arabkheradmand A Garajei H Mahmudzadeh M Shirkhoda M Motiee-Langroudi Z Mirzajani J Zebardast A Montazeri 2019 Evaluation of quality of life in patients with oral cancer after mandibular resection: comparing no reconstruction, reconstruction with plate, and reconstruction with flap Medicine 98 e17431 10.1097/md.0000000000017431 10.1097/md.0000000000017431 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

