CARM1 hypermethylates the NuRD chromatin remodeling complex to promote cell cycle gene expression and breast cancer development
- PMID: 38676947
- PMCID: PMC11229315
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae329
CARM1 hypermethylates the NuRD chromatin remodeling complex to promote cell cycle gene expression and breast cancer development
Abstract
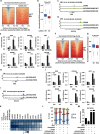
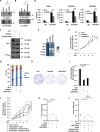
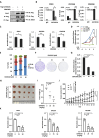
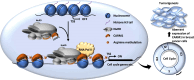
Protein arginine methyltransferase CARM1 has been shown to methylate a large number of non-histone proteins, and play important roles in gene transcriptional activation, cell cycle progress, and tumorigenesis. However, the critical substrates through which CARM1 exerts its functions remain to be fully characterized. Here, we reported that CARM1 directly interacts with the GATAD2A/2B subunit in the nucleosome remodeling and deacetylase (NuRD) complex, expanding the activities of NuRD to include protein arginine methylation. CARM1 and NuRD bind and activate a large cohort of genes with implications in cell cycle control to facilitate the G1 to S phase transition. This gene activation process requires CARM1 to hypermethylate GATAD2A/2B at a cluster of arginines, which is critical for the recruitment of the NuRD complex. The clinical significance of this gene activation mechanism is underscored by the high expression of CARM1 and NuRD in breast cancers, and the fact that knockdown CARM1 and NuRD inhibits cancer cell growth in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo. Targeting CARM1-mediated GATAD2A/2B methylation with CARM1 specific inhibitors potently inhibit breast cancer cell growth in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo. These findings reveal a gene activation program that requires arginine methylation established by CARM1 on a key chromatin remodeler, and targeting such methylation might represent a promising therapeutic avenue in the clinic.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A role for CARM1-mediated histone H3 arginine methylation in protecting histone acetylation by releasing corepressors from chromatin.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e34692. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034692. Epub 2012 Jun 18. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22723830 Free PMC article.
-
A hypermethylation strategy utilized by enhancer-bound CARM1 to promote estrogen receptor α-dependent transcriptional activation and breast carcinogenesis.Theranostics. 2020 Feb 10;10(8):3451-3473. doi: 10.7150/thno.39241. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32206101 Free PMC article.
-
PELP1 oncogenic functions involve CARM1 regulation.Carcinogenesis. 2013 Jul;34(7):1468-75. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgt091. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Carcinogenesis. 2013. PMID: 23486015 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Arginine Methyltransferase CARM1 in Human Breast Cancer.Endocrinology. 2024 Jul 1;165(8):bqae068. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqae068. Endocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38878278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The emerging role of CARM1 in cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Oct;47(5):1503-1522. doi: 10.1007/s13402-024-00943-9. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 38619752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of protein arginine methyltransferase in osteoporosis: a narrative review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Apr 24;13:1453624. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1453624. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40342926 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chen D., Ma H., Hong H., Koh S.S., Huang S.M., Schurter B.T., Aswad D.W., Stallcup M.R.. Regulation of transcription by a protein methyltransferase. Science. 1999; 284:2174–2177. - PubMed
-
- Teyssier C., Chen D., Stallcup M.R.. Requirement for multiple domains of the protein arginine methyltransferase CARM1 in its transcriptional coactivator function. J. Biol. Chem. 2002; 277:46066–46072. - PubMed
-
- Larsen S.C., Sylvestersen K.B., Mund A., Lyon D., Mullari M., Madsen M.V., Daniel J.A., Jensen L.J., Nielsen M.L.. Proteome-wide analysis of arginine monomethylation reveals widespread occurrence in human cells. Sci. Signal. 2016; 9:rs9. - PubMed
-
- Peng B.L., Li W.J., Ding J.C., He Y.H., Ran T., Xie B.L., Wang Z.R., Shen H.F., Xiao R.Q., Gao W.W.et al. .. A hypermethylation strategy utilized by enhancer-bound CARM1 to promote estrogen receptor alpha-dependent transcriptional activation and breast carcinogenesis. Theranostics. 2020; 10:3451–3473. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82125028/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2020YFA0112300/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 2020J02004/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province of China
- 20720190145/Fundamental Research Funds for the Central University
- 2022M712661/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

