Integrative analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics to uncover biomarkers in sepsis
- PMID: 38678059
- PMCID: PMC11055861
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-59400-0
Integrative analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics to uncover biomarkers in sepsis
Abstract
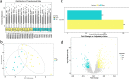
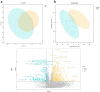
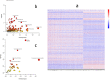
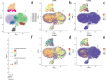
To utilize metabolomics in conjunction with RNA sequencing to identify biomarkers in the blood of sepsis patients and discover novel targets for diagnosing and treating sepsis. In January 2019 and December 2020, blood samples were collected from a cohort of 16 patients diagnosed with sepsis and 11 patients diagnosed with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). Non-targeted metabolomics analysis was conducted using liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS technology), while gene sequencing was performed using RNA sequencing. Afterward, the metabolite data and sequencing data underwent quality control and difference analysis, with a fold change (FC) greater than or equal to 2 and a false discovery rate (FDR) less than 0.05.Co-analysis was then performed to identify differential factors with consistent expression trends based on the metabolic pathway context; KEGG enrichment analysis was performed on the crossover factors, and Meta-analysis of the targets was performed at the transcriptome level using the public dataset. In the end, a total of five samples of single nucleated cells from peripheral blood (two normal controls, one with systemic inflammatory response syndrome, and two with sepsis) were collected and examined to determine the cellular location of the essential genes using 10× single cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq). A total of 485 genes and 1083 metabolites were found to be differentially expressed in the sepsis group compared to the SIRS group. Among these, 40 genes were found to be differentially expressed in both the metabolome and transcriptome. Functional enrichment analysis revealed that these genes were primarily involved in biological processes related to inflammatory response, immune regulation, and amino acid metabolism. Furthermore, a meta-analysis identified four genes, namely ITGAM, CD44, C3AR1, and IL2RG, which were highly expressed in the sepsis group compared to the normal group (P < 0.05). Additionally, scRNA-seq analysis revealed that the core genes ITGAM and C3AR1 were predominantly localized within the macrophage lineage. The primary genes ITGAM and C3AR1 exhibit predominant expression in macrophages, which play a significant role in inflammatory and immune responses. Moreover, these genes show elevated expression levels in the plasma of individuals with sepsis, indicating their potential as valuable subjects for further research in sepsis.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Metabolomics; RNA sequencing; Sepsis; Single-cell RNA sequencing.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer S, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet. 2020;395(10219):200–211. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

