The addition of bortezomib to rituximab, high-dose cytarabine and dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma-a randomized, open-label phase III trial of the European mantle cell lymphoma network
- PMID: 38678093
- PMCID: PMC11147755
- DOI: 10.1038/s41375-024-02254-2
The addition of bortezomib to rituximab, high-dose cytarabine and dexamethasone in relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma-a randomized, open-label phase III trial of the European mantle cell lymphoma network
Abstract
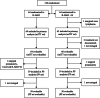
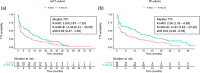
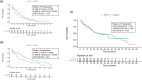
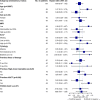
The therapy of relapsed or refractory (r/r) mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients remains a major clinical challenge to date. We conducted a randomized, open-label, parallel-group phase-III trial hypothesizing superior efficacy of rituximab, high-dose cytarabine and dexamethasone with bortezomib (R-HAD + B) versus without (R-HAD) in r/r MCL ineligible for or relapsed after autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT). Primary endpoint was time to treatment failure (TTF), secondary endpoints included response rates, progression free survival, overall survival, and safety. In total, 128 of 175 planned patients were randomized to R-HAD + B (n = 64) or R-HAD (n = 64). Median TTF was 12 vs. 2.6 months (p = 0.045, MIPI-adjusted HR 0.69; 95%CI 0.47-1.02). Overall and complete response rates were 63 vs. 45% (p = 0.049) and 42 vs. 19% (p = 0.0062). A significant treatment effect was seen in the subgroup of patients >65 years (aHR 0.48, 0.29-0.79) and without previous ASCT (aHR 0.52, 0.28-0.96). Toxicity was mostly hematological and attributable to the chemotherapeutic backbone. Grade ≥3 leukocytopenia and lymphocytopenia were more common in R-HAD + B without differences in severe infections between both arms. Bortezomib in combination with chemotherapy can be effective in r/r MCL and should be evaluated further as a therapeutic option, especially if therapy with BTK inhibitors is not an option. Trial registration: NCT01449344.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JD served on advisory boards and received speakers’ honoraria from Janssen and Roche. C Schmidt received support for consultancy from BMS and Janssen, honoraria from BMS and Astra Zeneca and meeting or travel support from Kite Gilead. SS received advisory board honoraria, research support, travel support, speaker fees and support for trial participation from AbbVie, Acerta, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BeiGene, BMS, Celgene, Gilead, GSK, Hoffmann-La Roche, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Sunesis. C Scholz received consultancy fees from GILEAD, Incyte, Janssen-Cilag, MSD, Miltenyi Biotec, Novartis, Roche, Takeda, honoraria from BeiGene, GILEAD, Janssen-Cilag, Roche, Lilly, Takeda and travel expenses from BeiGene, Roche and Takeda. MH received honoraria from Novartis, Sobi, Gilead Sciences and Falk Foundation, has consulted for Novartis, BMS/Celgene, Gilead Sciences, Pfizer, Incyte, Sanofi/Aventis, Roche, Amgen, Sobi and Janssen. VR received research funding from Astex and GSK, consulting fees from Servier, honoraria from Abbvie and Pharmamar, meeting/travel support from AZD and GSK and participated on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board of BMS, AZD and Gilead. MD received research funding from Abbvie, Bayer, BMS/Celgene, Kite/Gilead, Janssen and Roche, speakers’ honoraria from Astra Zeneca, Beigene, Gilead/Kite, Janssen, Lilly, 1 Novartis and Roche, and served on scientific advisory boards of Abbvie, Astra Zeneca, Beigene, BMS/Celgene, Gilead/Kite, Janssen, Lilly/Loxo, Novartis and Roche. All remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hoster E, Rosenwald A, Berger F, Bernd HW, Hartmann S, Loddenkemper C, et al. Prognostic value of Ki-67 index, cytology, and growth pattern in mantle-cell lymphoma: results from randomized trials of the european mantle cell lymphoma network. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34:1386–94. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.8387. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

