Epidemiology, Patient Characteristics, and Treatment Patterns of Myasthenia Gravis in Taiwan: A Population-Based Study
- PMID: 38678112
- PMCID: PMC11136923
- DOI: 10.1007/s40120-024-00619-4
Epidemiology, Patient Characteristics, and Treatment Patterns of Myasthenia Gravis in Taiwan: A Population-Based Study
Abstract
Introduction: Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic neuromuscular disease leading to significant disease burden. This study aimed to investigate the epidemiology of MG in Taiwan.
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted using the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database. Prevalent patients with MG diagnosis (either ocular or generalized MG) from 2013 to 2019 were identified, and 2813 patients with initial MG diagnosis from 2014 to 2019 were further defined as the incident cohort. Patient characteristics, treatment patterns, and the occurrence of MG-related events were analyzed.
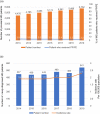
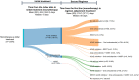
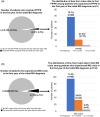
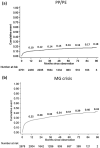
Results: The number of prevalent patients with MG increased from 4476 in 2013 to 5752 in 2019, with the prevalence rate increasing from 19 to 24 per 100,000 population. The incidence rate also slightly increased from 1.9 to 2.3 per 100,000 population during the study period. Almost all incident patients (99%, n = 2791) received MG-related treatment during the follow-up period. Among 1876 patients who received monotherapy as their initial treatment in the outpatient setting, the mean time from the index date to initial treatment was 48.8 (standard deviation 164.3) days, and most patients received acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (88.5%, n = 1661) as their initial treatment. During the first year after the index date, 133 (4.7%) incident patients experienced their first myasthenic crisis, and 96.2% of these events occurred within 3 months.
Conclusion: The prevalence of MG increased steadily in Taiwan, and the treatment of patients with MG was consistent with guidelines. Despite a high treatment rate, patients still experienced MG-related events, highlighting the limitation of current treatments and emphasizing the need for early intervention and novel treatment approaches.
Keywords: Disease burden; Epidemiology; Myasthenia gravis (MG); Myasthenic crisis; Treatment pattern.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Connie Hung and Amanda Kuo are employees of UCB Pharma. Hung-Wei Lin, and Kai-Pei Chou are employees of IQVIA Solutions Taiwan Ltd. Li-Shan Jian is a former employee of IQVIA Solutions Taiwan Ltd., and the work was done while affiliated with IQVIA Solutions Taiwan Ltd.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

