Outcome assessment methods of bioactive and biodegradable materials as pulpotomy agents in primary and permanent teeth: a scoping review
- PMID: 38678210
- PMCID: PMC11055312
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04221-w
Outcome assessment methods of bioactive and biodegradable materials as pulpotomy agents in primary and permanent teeth: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Pulpotomy procedures aiming to preserve and regenerate the dentin-pulp complex have recently increased exponentially due to developments in the field of biomaterials and tissue engineering in primary and permanent teeth. Although the number of studies in this domain has increased, there is still scarcity of evidence in the current literature.
Objectives: (1) Report the methods of outcome assessment of pulpotomy clinical trials in both primary and permanent teeth; (2) Identify the various bioactive agents and biodegradable scaffolds used in pulpotomy clinical trials in both primary and permanent teeth.
Materials and methods: A scoping review of the literature was performed, including a search of primary studies on PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, ProQuest and Clinicaltrials.gov. A search for controlled trials or randomized controlled trials published between 2012 and 2023 involving primary or permanent teeth receiving partial or full pulpotomy procedures using bioactive/regenerative capping materials was performed.
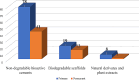
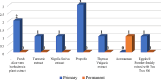
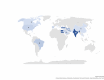
Results: 127 studies out of 1038 articles fulfilled all the inclusion criteria and were included in the current scoping review. More than 90% of the studies assessed clinical and radiographic outcomes. Histological, microbiological, or inflammatory outcomes were measured in only 9.4% of all included studies. Majority of the studies (67.7%) involved primary teeth. 119 studies used non-degradable bioactive cements, while biodegradable scaffolds were used by 32 studies, natural derivates and plant extracts studies were used in only 7 studies. Between 2012 (4 studies) and 2023 (11 studies), there was a general increase in the number of articles published. India, Egypt, Turkey, and Iran were found to have the highest total number of articles published (28, 28,16 and 10 respectively).
Conclusions: Pulpotomy studies in both primary and permanent teeth relied mainly on subjective clinical and radiographic outcome assessment methods and seldom analyzed pulpal inflammatory status objectively. The use of biodegradable scaffolds for pulpotomy treatments has been increasing with an apparent global distribution of most of these studies in low- to middle-income countries. However, the development of a set of predictable outcome measures as well as long-term evidence from well conducted clinical trials for novel pulpotomy dressing materials are still required.
Keywords: Bioactive agents; Biodegradable scaffolds; Clinical outcome; Histological outcome; Permanent teeth; Primary teeth; Pulpotomy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Treatment outcomes of pulpotomy in primary molars using two endodontic biomaterials. A 2-year randomised clinical trial.Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2011 Sep;12(3):189-93. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2011. PMID: 22077689 Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of pulpotomy in managing carious exposure in mature permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Dent. 2024 Nov;150:105392. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2024.105392. Epub 2024 Oct 5. J Dent. 2024. PMID: 39369880
-
A randomized controlled trial of various MTA materials for partial pulpotomy in permanent teeth.J Dent. 2017 May;60:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2016.07.015. Epub 2016 Jul 27. J Dent. 2017. PMID: 27472957 Clinical Trial.
-
Materials for pulpotomy in immature permanent teeth: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2019 Oct 23;19(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12903-019-0917-z. BMC Oral Health. 2019. PMID: 31647004 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative evaluation of formocresol and mineral trioxide aggregate as pulpotomy agents in deciduous teeth.Indian J Dent Res. 2011 May-Jun;22(3):385-90. doi: 10.4103/0970-9290.87058. Indian J Dent Res. 2011. PMID: 22048576 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Endocyn on Dental Pulp Stem Cells (DPSCs): A Pilot Study of Endodontic Irrigant Effects.Methods Protoc. 2025 Feb 11;8(1):18. doi: 10.3390/mps8010018. Methods Protoc. 2025. PMID: 39997642 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Research Productivity in Pulpotomy: A Bibliometric Analysis.Cureus. 2024 Nov 2;16(11):e72893. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72893. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39624532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Survival analysis of pulpotomy versus pulpectomy in primary molars with carious pulp exposure: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Nov 13;24(1):1370. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05008-9. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39538161 Free PMC article.
References
-
- El karim Ikhlas A, CPR, About Imad, Tomson Phillip L, Lundy Fionnuala T. Duncan Henry F. Deciphering Reparative Processes in the Inflamed Dental Pulp. 2021;2.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

