Associations between non-insulin-based insulin resistance indices and heart failure prevalence in overweight/obesity adults without diabetes mellitus: evidence from the NHANES 2001-2018
- PMID: 38678275
- PMCID: PMC11055335
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-024-02114-z
Associations between non-insulin-based insulin resistance indices and heart failure prevalence in overweight/obesity adults without diabetes mellitus: evidence from the NHANES 2001-2018
Abstract
Background: The triglyceride glucose (TyG) index and triglyceride-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio are recognized as simple non-insulin-based insulin resistance indices. Our study aimed to explore the relationship between these two indicators and heart failure (HF) in overweight or obesity individuals without diabetes.
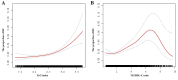
Methods: This cross-sectional study selected 13,473 participants from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001-2018 dataset. Weighted multivariable logistic regression and subgroup analysis were employed to evaluate the relationships between TyG index, TG/HDL-C ratio, and HF prevalence, respectively. Additionally, smooth curve fitting was utilized to analyze the dose-response relationships.
Results: A total of 13,473 obesity or overweight people without diabetes were included in this study through screening, among whom 291 (2.16%) had comorbid HF. The results of multivariable logistic regression suggested that the highest TyG index (OR = 2.4, 95% CI = 1.4-4.2, p = 0.002) and the highest TG/HDL-C ratio (OR = 1.2, 95% CI = 1.1-1.3, p < 0.001) both increased the prevalence of HF, especially in the non-Hispanic population. Dose-response relationships suggested nonlinear relationships between these two indicators and HF.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrated that elevated TyG index and TG/HDL-C ratio were closely associated with the prevalence of HF, and both exhibited nonlinear relationships with HF prevalence in overweight/obesity adults without diabetes. Based on these findings, additional prospective studies are needed for further validation.
Keywords: Heart failure; Overweight/obesity; Triglyceride-glucose index; Triglyceride-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Associations between triglyceride-glucose index combined with waist circumference and heart failure in individuals with different body mass indices: a cross-sectional study using NHANES 2011-2020 data.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Mar 7;24(1):87. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02476-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 40055792 Free PMC article.
-
Association between sarcopenic obesity and osteoarthritis: The potential mediating role of insulin resistance.Exp Gerontol. 2024 Nov;197:112611. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112611. Epub 2024 Oct 21. Exp Gerontol. 2024. PMID: 39423937
-
Inverse association of triglyceride-glucose and triglyceride/HDL-c indexes with serum 25(OH) vitamin D levels in US adults.Lipids. 2025 May;60(3):155-163. doi: 10.1002/lipd.12429. Epub 2025 Jan 19. Lipids. 2025. PMID: 39829058
-
Comparison of different insulin resistance surrogates to predict hyperuricemia among U.S. non-diabetic adults.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Dec 15;13:1028167. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1028167. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36589794 Free PMC article.
-
Triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a predictor similar to the triglyceride-glucose index for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome using International Diabetes Federation criteria of insulin resistance in obese adolescents: a cross-sectional study.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020 May 24;33(6):777-784. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2019-0310. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020. PMID: 32447329
Cited by
-
The Triglyceride/HDL Ratio as a Surrogate Biomarker for Insulin Resistance.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 5;12(7):1493. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071493. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association Between Triglyceride/High-Density Lipoprotein Ratio and Incidence Risk of Heart Failure: A Population-Based Cohort Study.J Clin Med. 2025 Feb 1;14(3):950. doi: 10.3390/jcm14030950. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 39941621 Free PMC article.
-
Obesity as Inducer of Cognitive Function Decline via Dysbiosis of Gut Microbiota in Rats.Brain Sci. 2024 Aug 12;14(8):807. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14080807. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39199499 Free PMC article.
-
The levels of systemic inflammatory markers exhibit a positive correlation with the occurrence of heart failure: a cross-sectional study from NHANES.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Oct 11;11:1457534. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2024.1457534. eCollection 2024. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39465132 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Different Insulin Resistance Indices and Heart Failure in US Adults With Diabetes Mellitus.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2024 Nov;29(6):e70035. doi: 10.1111/anec.70035. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2024. PMID: 39545717 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Federation WO. World Obesity Atlas 2023. https://dataworldobesityorg/publications/?cat=19 2023.
-
- Kenchaiah S, Pocock SJ, Wang D, Finn PV, Zornoff LA, Skali H, Pfeffer MA, Yusuf S, Swedberg K, Michelson EL, et al. Body mass index and prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure: insights from the Candesartan in Heart failure: Assessment of reduction in mortality and morbidity (CHARM) program. Circulation. 2007;116(6):627–36. - PubMed
-
- Son TK, Toan NH, Thang N, Le Trong Tuong H, Tien HA, Thuy NH, Van Minh H, Valensi P. Prediabetes and insulin resistance in a population of patients with heart failure and reduced or preserved ejection fraction but without diabetes, overweight or hypertension. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022;21(1):75. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

