Kelvin-Helmholtz-induced mixing in multi-fluid partially ionized plasmas
- PMID: 38679056
- PMCID: PMC11056270
- DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0227
Kelvin-Helmholtz-induced mixing in multi-fluid partially ionized plasmas
Abstract
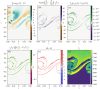
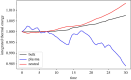
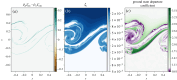
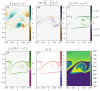
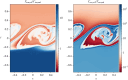
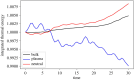
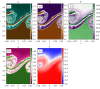
Turbulence is a fundamental process that drives mixing and energy redistribution across a wide range of astrophysical systems. For warm ([Formula: see text]) plasma, the material is partially ionized, consisting of both ionized and neutral species. The interactions between ionized and neutral species are thought to play a key role in heating (or cooling) of partially ionized plasmas. Here, mixing is studied in a two-fluid partially ionized plasma undergoing the shear-driven Kelvin-Helmholtz instability to evaluate the thermal processes within the mixing layer. Two-dimensional numerical simulations are performed using the open-source (PIP) code that solves for a two-fluid plasma consisting of a charge-neutral plasma and multiple excited states of neutral hydrogen. Both collisional and radiative ionization and recombination are included. In the mixing layer, a complex array of ionization and recombination processes occur as the cooler layer joins the hotter layer, and vice versa. In localized areas of the mixing layer, the temperature exceeds the initial temperatures of either layer with heating dominated by collisional recombinations over turbulent dissipation. The mixing layer is in approximate ionization-recombination equilibrium, however the obtained equilibrium is different to the Saha-Boltzmann local thermal equilibrium. The dynamic mixing processes may be important in determining the ionization states, and with that intensities of spectral lines, of observed mixing layers. This article is part of the theme issue 'Partially ionized plasma of the solar atmosphere: recent advances and future pathways'.
Keywords: mixing; partial ionization; shear instabilities; two-fluid.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Radiative loss and ion-neutral collisional effects in astrophysical plasmas.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024 Jun 9;382(2272):20230217. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0217. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024. PMID: 38679058
-
Future prospects for partially ionized solar plasmas: the prominence case.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024 Jun 9;382(2272):20230225. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0225. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024. PMID: 38679050 Review.
-
Parametric resonance of Alfvén waves driven by ionization-recombination waves in the weakly ionized solar atmosphere.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024 Jun 9;382(2272):20230226. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0226. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024. PMID: 38679051 Free PMC article.
-
Mixing, heating and ion-neutral decoupling induced by Rayleigh-Taylor instability in prominence-corona transition regions.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024 Jun 9;382(2272):20230417. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0417. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024. PMID: 38679055
-
Partial ionization of plasma in solar prominences.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024 Jun 9;382(2272):20230221. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0221. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024. PMID: 38679046 Review.
Cited by
-
Partially ionized plasma of the solar atmosphere: recent advances and future pathways.Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024 Jun 9;382(2272):20230230. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2023.0230. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Philos Trans A Math Phys Eng Sci. 2024. PMID: 38679048 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Magyar N, Van Doorsselaere T. 2016. Damping of nonlinear standing kink oscillations: a numerical study. Astron. Astrophys. 595, A81. (10.1051/0004-6361/201629010) - DOI
-
- Hillier A, Arregui I. 2019. Coronal cooling as a result of mixing by the nonlinear Kelvin-Helmholtz instability. Astrophys. J. 885, 101. (10.3847/1538-4357/ab4795) - DOI
-
- Hillier A, Snow B, Arregui I. 2023. The role of cooling induced by mixing in the mass and energy cycles of the solar atmosphere. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 520, 1738-1747. (10.1093/mnras/stad234) - DOI
-
- Arber TD, Brady CS, Shelyag S. 2016. Alfvén wave heating of the solar chromosphere: 1.5d models. Astrophys. J. 817, 94. (10.3847/0004-637X/817/2/94) - DOI
-
- Soler R, Ballester JL. 2022. Theory of fluid instabilities in partially ionized plasmas: an overview. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 9, 789083. (10.3389/fspas.2022.789083) - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

